Definition of Persian Empire
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Cecilia Bembibre, in Dec. 2009
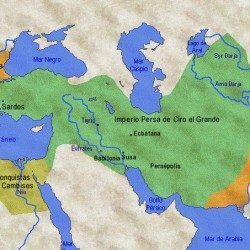 The Persian Empire has been one of the largest in history, managing to occupy an extensive territory which included the current territories of Iran, Iraq, part of Egypt, Turkey, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Armenia, Turkmenistan, Yemen, Oman, Syria, Jordan, Lebanon and others. In addition, its power was maintained for centuries thanks to being one of the military and political powers of antiquity.
The Persian Empire has been one of the largest in history, managing to occupy an extensive territory which included the current territories of Iran, Iraq, part of Egypt, Turkey, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Armenia, Turkmenistan, Yemen, Oman, Syria, Jordan, Lebanon and others. In addition, its power was maintained for centuries thanks to being one of the military and political powers of antiquity.
The Persians are originally Indo-European and it is estimated that their settlement in what is now the Middle East it began around 2000 BC, at which time there were numerous Indo-European invasions and displacements throughout the region. The Persians settled in the territory that today belongs to Iran and that would then be known as Persia (hence the Iranians consider themselves Persians). The Persian settlement would grow over time and what we know today as the great Persian Empire would be a impressive military work that would begin with the Persian Achaemenid dynasty (which would reign between 705 and 675 a. C.) and that it would reach its maximum
expression and relevance with the emperor Cyrus the Great (between the years 559 and 530 a. C.). Other emperors of great importance would be Darío and his son Xerxes.The Persian Empire was characterized by being highly centralized and by falling almost exclusively on the person of the emperor, who concentrated all power. The territory of the empire was organized in satrapies that were kind of provinces with a minimum degree of autonomy since they always had to respond to the central power. Obviously, military power was one of the strongholds of the Persian Empire and through the use of that power the civilization Persian was able to conquer numerous societies in the region and assimilate them to his empire immediately. One of the most important capitals of the empire was the beautiful city of Persepolis.
Regardless of its achievements and its political-military relevance, the Persian Empire also meant to impose itself culturally in the Middle East region. Their religion (in worship of the god Zoroaster) supposed the I respect by values such as truth and Justice, at the same time as the honesty and the integrity of its rulers were what allowed it to continue to remain in power. The Persians held numerous and abundant festivities in honor of the Persian gods and among their traditions More important we find that of polygamy, which allowed a man to be married to many women at the same time. Finally, in the art, the Persians were characterized by the realization of monumental constructions that were decorated by impressive and lively sculptures of mythological animals with the heads of human beings and winged ones.
Themes in Persian Empire


