Definition of Atomic Number
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Javier Navarro, in Nov. 2016
 In relation to the atoms that make up matter, they are formed by a core, in which are the protons with a positive charge and the neutrons with a negative charge and, on the other hand, around the nucleus are the electrons, which have a negative charge.
In relation to the atoms that make up matter, they are formed by a core, in which are the protons with a positive charge and the neutrons with a negative charge and, on the other hand, around the nucleus are the electrons, which have a negative charge.
All elements have the same number of protons as electrons and that number is what determines the atomic number of an element. This implies that the atomic number refers to the total number of protons in an atom. Consequently, the atomic number expresses what is the identity of an element.
Atomic number and mass number
To represent the atomic number, it is placed before the element. Thus, 5B indicates that the atomic number of boron is 5 and, therefore, boron is an element with 5 electrons circling around the nucleus and with 5 other protons inside the nucleus. Boron, on the other hand, has a series of neutrons, which are calculated by subtracting the mass number minus the atomic number. Thus, if boron has 11 neutrons and we subtract its corresponding atomic number, we will obtain that its mass number is 6. As for its indication, the mass number is placed on top of the atomic number of each element. With regard to terminology, the atomic number is symbolized with the
lyrics Z and the mass number with the letter A.If we take hydrogen as a reference, its atomic number is 1 and 1H is represented, thus indicating that there is a proton in the nucleus of a hydrogen atom. If we talk about an atom neutral, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons, since in a neutral atom there is no charge total and the positive charges of the protons are balanced with the negative charges of the protons. electrons.
The periodic table of the elements and the atomic number
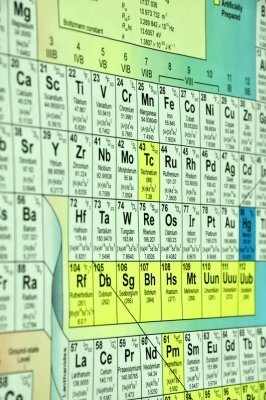 From the point of view of matter, everything that exists can be expressed with the language of chemistry. To understand the diversity from elements of nature it results essential resort to periodic table.
From the point of view of matter, everything that exists can be expressed with the language of chemistry. To understand the diversity from elements of nature it results essential resort to periodic table.
In the periodic table the elements are grouped and ordered according to their atomic number. The elements of this table can be divided into three large groups: metals, non-metals and metalloids. Metals are great conductors of electricity and heat, while nonmetals represent the opposite and metalloids present intermediate characteristics between metals and nonmetals.
Photos: Fotolia - nadjagellermann / photostock77
Topics in Atomic Number


