Definition of Radioactive Isotopes
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Dra. Maria de Andrade, CMDF 21528, MSDS 55658., at Mar. 2015
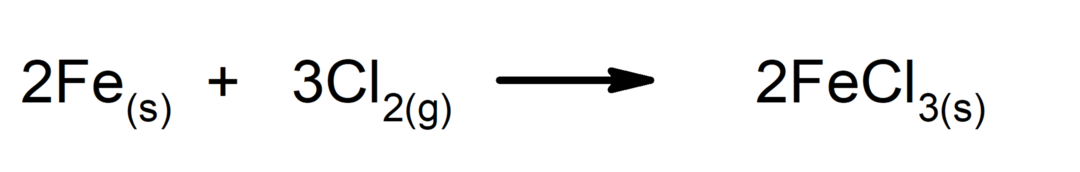
 The Radioactive Isotopes are atoms of an element that have been modified in such a way that a greater number of neutrons are found in its nucleus than in the original element, therefore this new atom has the same number of electrons in its outer shell, the same atomic number that corresponds to the number of protons in the nucleus, which defines its location on the periodic table, but different atomic mass or atomic weight since this last value corresponds to the sum of neutrons and protons in the nucleus.
The Radioactive Isotopes are atoms of an element that have been modified in such a way that a greater number of neutrons are found in its nucleus than in the original element, therefore this new atom has the same number of electrons in its outer shell, the same atomic number that corresponds to the number of protons in the nucleus, which defines its location on the periodic table, but different atomic mass or atomic weight since this last value corresponds to the sum of neutrons and protons in the nucleus.
Each of the different types of atoms have their isotopes, even the same atom can have many types of isotopes, some of them are stable but others, as is the case uranium, they are quite unstable so the atom spontaneously emits radiation while it becomes a more stable atom which makes it called an isotope radioactive. It is probable that after a first decomposition of the nucleus, the atom will not be able to stabilize, so the process continues until it decomposes into a new one. atom, this process can occur several times until stability is achieved, the successive atoms that are obtained in this process are known as a series or
family radioactive.Many isotopes are normally found in nature, however they can also be produced in nuclear laboratories by bombarding the atoms of a certain element with particles subatomic. In order to identify them, a nomenclature was created to identify them, which establishes that when symbol of the element, a subscript is placed on the left with its atomic number and a superscript also on the left with the mass number, This is cumbersome at times, so another accepted nomenclature is to place the name of the element followed by a hyphen and then Following the mass number, an example would be carbon-14 which corresponds to one of the best known radioactive isotopes such as Carbon-14.
Radioactive isotopes are widely used in different industrial processes and even in sciences such as medicine.
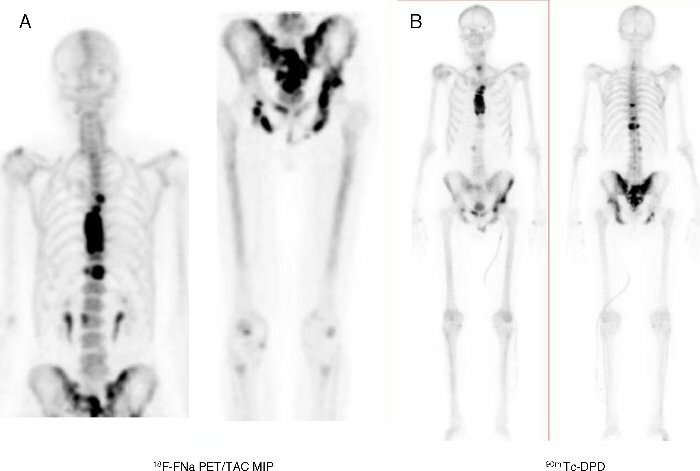 In the case of medicine, the branch known as nuclear medicine is based on the use of radioactive isotopes both for diagnostic purposes and for the treatment of some conditions. From the point of view of diagnosis one of the most used is in technesium-99, used in the study of Bone Scintigraphy, in order to obtain images of the skeleton showing increased uptake due to lesions secondary to metabolic bone problems as well as the presence of metastases from some tumors. Some isotopes such as cobalt-60 are used in a type of cancer treatment known as radiotherapy for their property of emitting radiation capable of killing tumor cells.
In the case of medicine, the branch known as nuclear medicine is based on the use of radioactive isotopes both for diagnostic purposes and for the treatment of some conditions. From the point of view of diagnosis one of the most used is in technesium-99, used in the study of Bone Scintigraphy, in order to obtain images of the skeleton showing increased uptake due to lesions secondary to metabolic bone problems as well as the presence of metastases from some tumors. Some isotopes such as cobalt-60 are used in a type of cancer treatment known as radiotherapy for their property of emitting radiation capable of killing tumor cells.
Another important use of radioactive isotopes is to establish the data of an organic sample, by measuring the levels of carbon-14 in it, in the processes of manufacturing made of plastic to give it a greater capacity for thermal and electrical insulation, as well as in the verification of welds of the pipes and ID of cracks, where iridium-192 is used.
Topics in Radioactive Isotopes