Definition of Mendel's Laws
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Florencia Ucha, in Dec. 2013
 Gregor Johann Mendel was a Austrian monk and naturalist that would go down to posterity for his contribution to the area of inheritancegeneticsduring the 19th century. Product of the study of him and investigation made the calls Mendel's Laws that will occupy us next and that is precisely the primordial theory on which genetics is based.
Gregor Johann Mendel was a Austrian monk and naturalist that would go down to posterity for his contribution to the area of inheritancegeneticsduring the 19th century. Product of the study of him and investigation made the calls Mendel's Laws that will occupy us next and that is precisely the primordial theory on which genetics is based.
It is worth mentioning that when Mendel published this work in the year 1866 It would not have the repercussion that his conclusions really deserved but it would be many years later, 34 years to be more precise, that those laws would be dusted from the chest by the botanists Hugo Marie de Vrie, Carl Correns and Erich von Tschermak.
It should be noted that Mendel's contribution is considered in science a milestone that could be comparable to the one he obtained Newton with his laws in the field of physics. But in addition, Mendel's laws are remarkable not only from a theoretical point of view but also that also from the epistemological and methodological point of view have known how to mark a before and after, without Doubts. Because the importance of methodical and precise experimentation is highlighted and then the results obtained are quantitatively overturned thanks to the
statistics, giving a very approximate panorama, and that of course, would surprise the science of those years.Then, Mendel's laws are a set of ground rules that explain the transmission of genetic inheritance from the organisms parents to their children and are also the pillar and base of genetics.
Meanwhile, the three laws would result from the experimentation that Mendel carried out crossing plants.
The first law is stated as Law of the uniformity of the hybrids of the first filial generation and maintains that if two pure races are crossed, the descendants of the first generation will all be the same physically and genetically and physically equal to one of his parents, regardless of the direction of the cross.
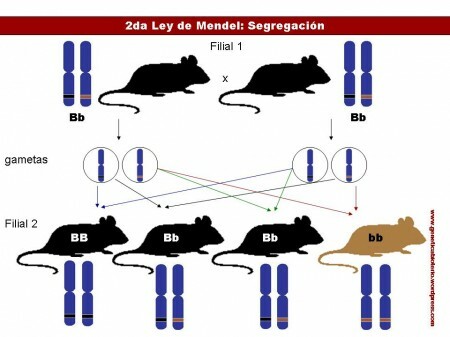
The second law called Law of the segregation of characters in the second filial generation indicates that at the time of gamete formation each allele of one pair is separated from the other to determine the Constitution genetics. This is that the maternal and paternal alleles appear combined in the descendant in question and ensure the variation.
And the third law, Law of the independence of hereditary characteristics which maintains that the various traits will be inherited independently of each other and there will be no relationship between them. For example, the inheritance pattern of one trait will not be affecting the other.
Topics in Mendel's Laws
