Concept in Definition ABC
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Javier Navarro, in Nov. 2018
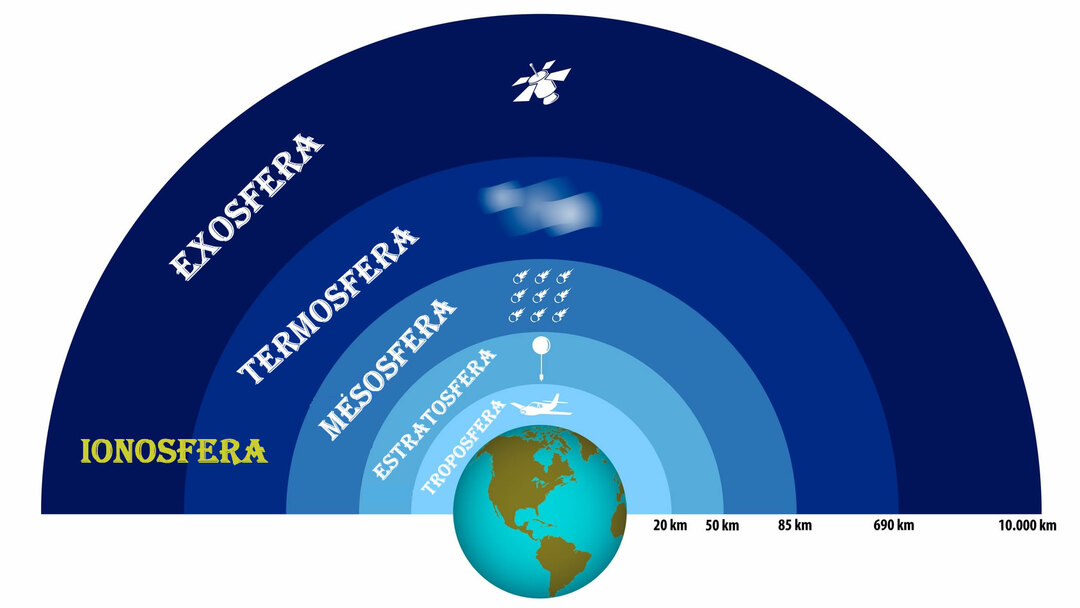 The atmosphere Is the set of gases that surround the Earth. In its outermost part there is a specific layer, the ionosphere. It receives this name because, being the layer closest to the Sun, an ionization process occurs due to the effect of solar radiation. In this framework, there is ionization as a consequence of the photons generated by the solar energy. At this level of the atmosphere the Energy of the Sun is so powerful that it causes the molecules to separate and the electrons scatter and float independently.
The atmosphere Is the set of gases that surround the Earth. In its outermost part there is a specific layer, the ionosphere. It receives this name because, being the layer closest to the Sun, an ionization process occurs due to the effect of solar radiation. In this framework, there is ionization as a consequence of the photons generated by the solar energy. At this level of the atmosphere the Energy of the Sun is so powerful that it causes the molecules to separate and the electrons scatter and float independently.
One of the layers of the Earth's atmosphere
In the ionosphere that surrounds the Earth there are electrons, atoms and molecules with electrical charges. This layer of the atmosphere is located between 50 and 1000 kilometers and constitutes less than 0.1% of the total mass that makes up the atmosphere.
The part closest to Earth is the troposphere, approximately 10 km from distance. Between the troposphere and the ionosphere there are three intermediate layers: mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere.
The ionosphere also has a subdivision. The so-called D layer is located about 50 km away and its main function is the protection of space radiation. Above this is the E layer, which is characterized by its ionized gas (ionization is not stable but depends on the angle from which the solar radiation originates).
Next comes the F layer, which is responsible for the propagation of electromagnetic waves (at this level there is an F1 layer and another F2, the first allows the absorption electromagnetic waves and the second is the one that allows the moment of maximum ionization in a day).
Current communications would not be possible if the ionosphere did not exist
 This external structure of the atmosphere is what allows the propagation of radio waves through space and, therefore, is essential for systems of communication and for navigation. This layer allows radio waves to bounce back and shortwave stations to send their transmissions beyond the horizon. The ionosphere deflects signals from GPS satellites.
This external structure of the atmosphere is what allows the propagation of radio waves through space and, therefore, is essential for systems of communication and for navigation. This layer allows radio waves to bounce back and shortwave stations to send their transmissions beyond the horizon. The ionosphere deflects signals from GPS satellites.
It also acts as a protective layer of the Earth, since it is where meteorites are disintegrated before they reach the land surface.
Finally, its different layers have a direct effect on the geomagnetic field of the Earth (the study of the mechanisms of the ionosphere has already made it possible to improve the prediction of earthquakes).
The planet Earth is not the only one with this specific layer of the atmosphere, since the planet Mars and the Moon also count with its own ionosphere (it was the Soviets in the 1970s who first identified the ionosphere lunar).
Fotolia photos: Pablofdezr / Kittiphat
Topics in Ionosphere
