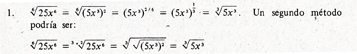40 Examples of Lexical Variants
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
Lexical variants
It is known at lexical variants to words that are characteristic of a certain place, but do not have the same meaning in another place, even if the cities are close and / or share the same language.
In other words, it can be defined at lexical variants such as the different use of linguistic elements but without modifying the concept or meaning of it. In the Spanish language it is common to observe this type of lexical variants.
Types of lexical variations
Geographic variations
Within the lexical variations, the geographical variants are the most visible. They are the variants used by the speakers that are modified by the region, zone or place where each one is making, in this way, local or geographical communicative adjustments. An example of this type of lexical variants is the dialect characteristic of each place.
Social variants
These variants occur within the same society and can understand the differences, for example, between different social classes and their way of speaking. Also in the social variants the type of cultural level of its speakers is discovered, so the Variation is not limited solely by economic factors but rather by sense of membership.
Contextual variation
Contextual variations are related to the context in which the speaker finds himself. Thus, when a speaker is in a formal setting she will use some resources or contextual lexical variants and when she is in another informal context, she will choose others.
In this context, it is important to take into account whether it is expressed orally (verbally) or whether the speaker is expressing itself written since both modes of communication also differ so that the sender of the message chooses one or other resources or lexical variants contextual.
Historical variation
This lexical variant will be determined by the social and contextual variant. Within this, the political and social history of each country or nation has weight since it will determine in some cases the use of one or other words with a certain charge (be it positive or negative) by the speakers of said language.
Examples of lexical variants
| 1 | car (Spain) | car (Mexico) |
| 2 | cerilla (Spain) | phosphorus (Mexico) |
| 3 | Bastoncillo (Spain) | Cotonete (Mexico) |
| 4 | Percha (Spain) | Hook (Mexico) |
| 5 | Chat (Spain) | Talk (Mexico) |
| 6 | Computer (Spain) | Computer (Mexico) |
| 7 | Mechero (Spain) | Lighter (Mexico) |
| 8 | Toad | Snitch |
| 9 | Crossing | Deal |
| 10 | Bacan (Argentina) | Good person |
| 11 | Yuta (Argentina) | Policeman |
| 12 | Mina (Argentina) | Pretty woman (Mexico) |
| 13 | Gil (Argentina) | Silly person who thinks he is very alive |
| 14 | Batidor (Argentina) | Snitch |
| 15 | Milico (Uruguay and Argentina) | Military |
| 16 | Cana (Uruguay) | Policeman |
| 17 | Chorro (Uruguay) | Thief |
| 18 | Chiva (Uruguay) | Bike |
| 19 | Calderin (Uruguay) | Net |
| 20 | Plate (Uruguay) | Currency |
| 21 | Dance (Uruguay) | Discotheque |
| 22 | Tata (Uruguay) | Grandpa |
| 23 | Tarasca (Uruguay) | Silver |
| 24 | Abonbado (Uruguay) | Fool |
| 25 | Arraca (Uruguay) | Careful |
| 26 | Miti (Uruguay) | Half |
| 27 | Laburo | Job |
| 28 | Cachad | Joke |
| 29 | Cart | Daring |
| 30 | Pen (Argentina) | Ballpoint |
| 31 | spherographic (Colombia) | |
| 32 | feather (Mexico) | |
| 33 | Avocado (Chile and Argentina) | Avocado (Mexico) |
| 34 | Poroto (Chile and Argentina) | Bean (Mexico) |
| 35 | Grapefruit (Argentina) | Grapefruit Mexico) |
| 36 | Ají (Argentina) | Chili (Mexico) |
| 37 | Bolillo (bread) (Mexico) | Cojinillo (Veracruz) |
| 38 | Pava (Argentina) | Teapot (Chile) |
| 39 | Rent (Argentina) | Leasing (Chile) |
| 40 | Turkey (Chile) | Guajolote (Mexico) |
| 41 | Banana (Ecuador) | Banana (Chile and Mexico) |
| 42 | Nene (Argentina) | Chavo (child) (Mexico) |