How are hydroxides formed? (with examples)
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
The hydroxides result from the combination of a metallic oxide (also called basic oxides) And the water. In this way, the composition of hydroxides is given by three elements: oxygen, hydrogen and the metal in question. In combination, the metal always act like cation and the hydroxide group (OH–) acts as an anion. For example:
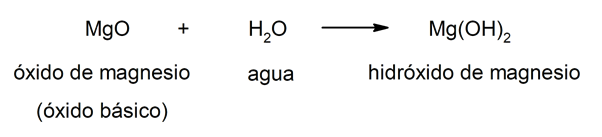
Hydroxides, in general, share a number of characteristics, such as presenting a bitter taste and being caustic. In addition, they are usually slippery to the touch and corrosive. On the other hand, they have some properties of detergents and soaps. Most are soluble in water and react with acids to produce you go out.
Some characteristics, on the other hand, are specific to each type of hydroxide, such as that of sodium (NaOH), which absorbs water, and mixed with quicklime (CaO) quickly absorbs carbon dioxide (CO2). For his part, calcium hydroxide (Ca (OH)2) it is obtained in the reaction of calcium oxide with water and also absorbs CO2. Another example is the iron (II) hydroxide (Fe (OH)2), which is a gelatinous compound and is practically insoluble in water.
Hydroxides are also called bases or alkalis, although these terms have been extended also for other substances with alkaline character and that are not hydroxides.
What are hydroxides used for?
The applications of hydroxides also vary between the different cases:
Nomenclatures
As well as to name other types of chemical compounds, there are different nomenclatures for hydroxides:
Examples of hydroxides
- Lead (II) hydroxide, Pb (OH)2, lead dihydroxide.
- Platinum (IV) hydroxide, Pt (OH)4, platinum tetrahydroxide.
- Vanadic hydroxide, V (OH)4, vanadium tetrahydroxide.
- Ferrous hydroxide, Fe (OH)2, iron dihydroxide.
- Lead (IV) hydroxide, Pb (OH)4, lead tetrahydroxide.
- Silver hydroxide, AgOH, silver hydroxide.
- Cobalt Hydroxide, Co (OH)2, cobalt dihydroxide.
- Manganese hydroxide, Mn (OH)3, manganese trihydroxide.
- Ferric hydroxide, Fe (OH)3, iron trihydroxide.
- Cupric hydroxide, Cu (OH)2, copper dihydroxide.
- Aluminum hydroxide, Al (OH)3, aluminum trihydroxide.
- Sodium hydroxide, NaOH, sodium hydroxide.
- Strontium hydroxide, Sr (OH)2, strontium dihydroxide.
- Magnesium hydroxide, Mg (OH)2, magnesium dihydroxide.
- Ammonium hydroxide, NH4OH, ammonium hydroxide.
- Cadmium hydroxide, Cd (OH)2, cadmium dihydroxide.
- Vanadic hydroxide, V (OH)3, vanadium trihydroxide.
- Mercuric hydroxide, Hg (OH)2, mercury dihydroxide.
- Cuprous hydroxide, CuOH, copper hydroxide.
- Lithium hydroxide, LiOH, lithium hydroxide.
Hydroxides sometimes have common names given by its more conventional uses: sodium hydroxide is also called caustic soda, potassium hydroxide is called caustic potash, calcium hydroxide which is called lime water or slaked lime and magnesium hydroxide which is called milk of magnesia.
Follow with:

