20 Examples of Covalent Bonds
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
A lots of chemical compounds are made up of molecules which, in turn, are composed of atoms. To form molecules, atoms join together by forming chemical links.
Chemical bonds are not all the same: they basically depend on the electronic characteristics of the atoms involved, their electronegativity values, among other factors. The most common types of link are: ionic bonds and the covalent bonds.
Covalent bonds are formed between non-metallic atoms of the same chemical element, between non-metallic atoms of different elements with an electronegativity difference less than or equal to 1.7 and between a non-metal and hydrogen. For example: dichloro, molecular oxygen, water.
The covalent bond is formed when two of these atoms share the electrons of their last energy level to fulfill the Octet rule, which establishes that the ions of the different chemical elements found in the Periodic table tend to complete their last energy levels with 8 electrons, so that the molecules can acquire a stability similar to that of the Noble gases.
Therefore, the way in which these substances or chemical compounds achieve stability is by sharing a pair of electrons (one from each atom). In this way, the shared pair of electrons is common to the two atoms and at the same time holds them together.
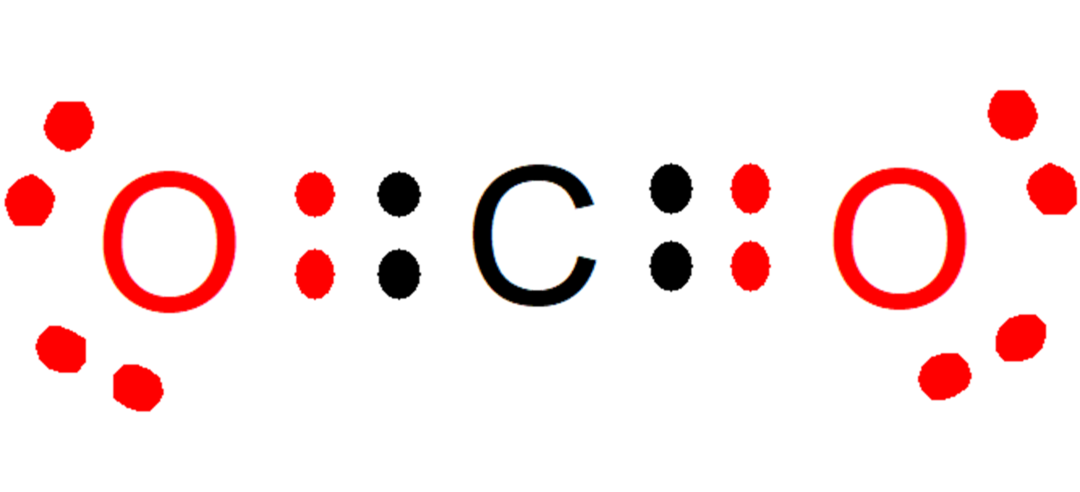
For example, in the carbon dioxide (CO2), each oxygen contributes two electrons (red color) to the bond with carbon, while carbon contributes two electrons (black color) to each bond with each oxygen. In the compound formed, 8 electrons remain on each atom, and thus the Rule of the Octet is fulfilled.
Types of links
There are fundamentally three types of covalent bonds, although it is important to clarify that no bond is absolutely covalent or absolutely ionic. All bonds have a certain percentage of covalent and ionic, in fact, ionic bonding is sometimes viewed as an "overstatement" of the covalent bond. In this sense, the following types of covalent bond may occur:
Substances composed of covalent molecules
The substances that contain covalent molecules can occur in any state of matter (solid, liquid or gaseous) and, in general, are poor conductors of hot and of the electricity.
There are molecular covalent substances and reticular covalent substances. The molecular covalents they have low boiling and melting points, are soluble in nonpolar solvents (such as benzene or carbon tetrachloride), and are soft in the solid state. The lattice covalents They form crystalline lattices, therefore they have higher melting and boiling points and are hard, insoluble solids.
Examples of covalent bonds
Numerous examples of compounds or substances containing covalent bonds can be given:
- Difluorine
- Dibromo
- Dichlor
- Diyodo
- Molecular oxygen
- Water
- Ammonia
- Carbon dioxide
- Methane
- Propane
- Glucose
- Molecular nitrogen
- Quartz
- Paraffin
- Diesel

Follow with:

