25 Examples of Predation
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
The predation is that biological relationship in which a species it needs to hunt another to survive, as it represents its only possibility of feeding. For example: the wolf is a predator of the elk, the gazelles are prey to the lion.
Predation always played a central role in everything Evolutionary process. With rare exceptions, the individuals belonging to the predatory relationship (called predator and prey) are of different species, and in some cases one predator can be at the same time prey to another, while a animal it can be the prey of various predators.
In predation, unlike many of the other biological relationships in nature, there are a single injured party and a single beneficiary: the predator needs the prey, while the prey may only need to protect itself from the danger that lurks. The fighting relationship includes visual or olfactory stimuli that the predator brings him closer to the prey, or a stalking that is carried out silently to avoid wasting energy.
It can serve you:
Types of relationships
The so-called biological interactions or relationships can be of different types:
Role in the evolutionary process
Predation has always been at the center of the evolutionary process. It is even part of the ecosystem, and the reductions in some species that this generates help to maintain a balanced nature: if a start to grow uncontrollably, possibly end up breaking the balance of the ecosystem.
Predators take care of keep the ecosystem balanced, and they are clever at controlling the number of members of the other species: they know perfectly well that if this one does not have possibilities of continuing to grow demographically, it will surely end up disappearing its greatest source of feeding.
Animal adaptations
It is frequent that they occur physical adaptations tending to take advantage of this fighting relationship, since the predator usually develops claws, sharp teeth, speed, agility, decides to hunt in a group and the surprise attack, while the prey defend themselves by running, hiding, even feigning their death and throwing substances with an unpleasant smell or taste.
Camouflage
One of the most striking circumstances of the predation process is camouflage, where an organism is capable of modify its color and shape becoming landscape-like, becoming more difficult for predator recognition in the case that it is a defensive attitude, or on the part of the prey if the change is on the part of the predator.
Animals, then, acquire a resembling inanimate objects like stones, trunks, leaves and branches, in such a way that they are almost impossible to appreciate unless a movement makes them especially striking: this behavior was replicated by humans for the jungle activities of hunting and hunting. war.
Examples of predatory relationships

- The lion, predator of impalas, zebras, buffalo (see image).
- The wolf, predator of the elk.
- Rattlesnakes, prey for badgers and some hawks.
- The American mink, a small predator of fish and mollusks.
- The gazelles, prey of the lion.
- The weasel, predator of rodents.
- The badger, a predator of worms.
- The tiger, predator of wild boars.
- The shark, predator of many fish.
- The mule deer, prey of the puma.
- The anaconda, the most important predatory amphibian.
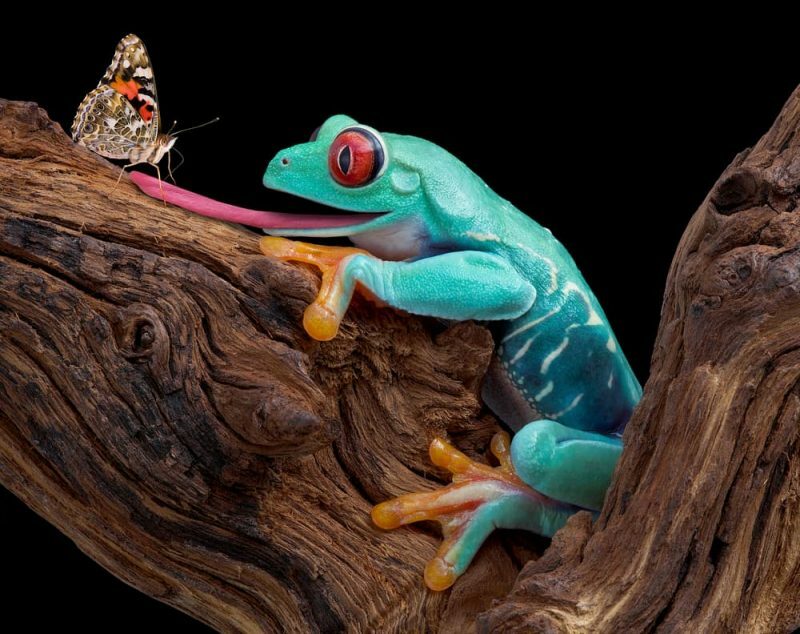
- The frog, predator of the beetle.
- The heron, predator of the crayfish.
- The hares, prey of the wolf and the fox.
- The tiger, predator of buffalo.
- The alligator, predator of some fish.
- The mice, prey of the jackal.
- The leming, prey of the arctic owl.
- The African lion, predator of a zebra.
- The tiger, predator of some fish.
- The jaguar, predator of deer.
- The seal, predator of some fish.
- The jackal, predator of birds.
- The jaguar, predator of tapirs.
- Flies and butterflies, prey for frogs.

Follow with: