Examples of Multicellular Organisms
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
The living beings (organisms), depending on the number of cells that compose them, can be considered unicellular (if they consist of a single cell) or multicellular (or multicellular, which are made up of two or more cells). For example: dolphin, hen, wheat, grass.
The cells they are considered the minimum units of life. They are units both in a morphological and functional aspect. They are morphological units because they are surrounded by an envelope, called the cell or cytoplasmic membrane.
Furthermore, cells are functional units because they constitute a complex biochemical system. As such, they have the ability to nourish and maintain their own metabolism, to grow and multiply from genetic material. contained in the nucleus, to differentiate (develop specific characteristics different from those of other cells) and to evolve.
All the characteristics of cells are shared by unicellular and multicellular organisms (also called multicellular).
Cell reproduction
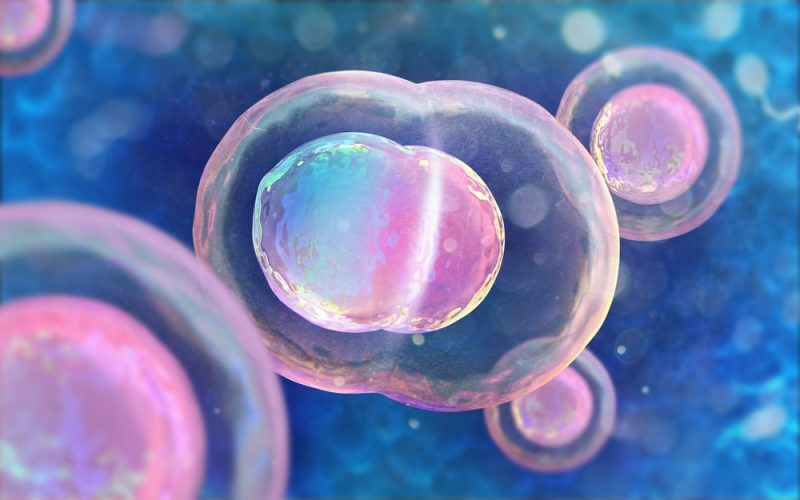
The multicellular organisms they arise initially from a single cell. Even human beings at the moment of conception are initially a cell. However, that cell immediately begins to multiply. Cells can reproduce through two processes:
From the above, it can be concluded that multicellular organisms obtain all of their cells (with the exception of sexual ones) from a single initial cell thanks to mitosis.
In multicellular organisms, not all cells are the same, but rather differentiate to fulfill different functions: for example, there are nerve cells, epithelial cells, cells muscle, etc. The specialized cells are organized into sets called fabrics, which in turn make up organs.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
In addition to differentiations, there are two main types of cells that in turn distinguish two different types of organisms:
Examples of multicellular organisms
- The human being. The different types of cells form the multiplicity of tissues that in turn form the circulatory, nervous, bone systems, etc.
- Crab. Like others crustaceans, part of its cells are differentiated to form an exoskeleton, a structure that covers and protects the animal.
- Dolphin. Aquatic mammal. Like all animals, it is made up of various types of eukaryotic animal cells.
- Wheat. Cereal of the grass family. It is made up of various types of eukaryotic plant cells.
- Swallow. Bird of migratory habits, pertaining to the family of the hirundínidos, of the order of the passerines.
- Grass. Like other monocotyledonous plants, its stem includes meristematic cells that allow it to increase its length after being cut.
- Chicken. Bird of the Phasianidae family. Like other birds, it is covered in feathers made up of specialized cells in the epidermis called keratinocytes.
- Salmon. Both marine and freshwater fish. Like most fish (bony or cartilaginous) its skin is covered in scales, specialized cells different from the scales of fish. reptiles.
- Temporaria frog. Amphibian anuran of the Ranidae family, which inhabits Europe and northwestern Asia.
- Green lizard. A species of lizard (reptile) of the family Teiidae. It is located in an ecozone that spans the Argentine, Bolivian and Paraguayan Chaco.
Of course, in addition to those mentioned, thousands of examples could be listed, since all the animals that exist are multicellular organisms. If you need more examples, you could visit the section of Vertebrate animals or Invertebrate animals.



