15 Examples of Simple, Double and Triple Bonds
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
In chemistry, when we talk about single, double and triple bonds we refer to three of the known forms of covalent bond, that is, of unions between atoms from the electron compartment of their last energy levels. There is also the dative covalent bond, in which case the electrons that are shared are contributed by only one of the atoms that form the bond.
Covalent bonds occur when two atoms are close enough to partially overlap their atomic orbitals (region of space where an electron is likely to be found around the nucleus), thus compensating for the simultaneous attractive and repulsive forces arising from its charges electrons (negative electrons repel each other but the positive charges of the atomic nuclei attract them) and acquiring a maximum stability that allows them to constitute a molecule.
When this happens, electron pairs that orbit the outermost layers of each atomic nucleus move towards the other until making it impossible to determine which atomic nucleus they belonged to.
Differences between covalent bond, ionic bond and metallic bond
Covalent bond types
Depending on the number of pairs of electrons shared between the atoms that form the bond, the covalent bonds will be simple (one pair), double (two pairs) or triple (three pairs). Each is usually represented by one, two or three lines between the symbols of each atom:
The number of single, double or triple bonds that an atom can form depends directly on its valence, that is, on the number of electrons it can share from its outermost shell.
In addition, depending on the degree of complexity of the bond, the molecule has more or less mobility (less mobility the more complex the bond) since the distance between the atoms is smaller and it is more difficult to break the bond, that is, more energy must be applied to achieve its breaking off.
Simple covalent bond examples
- Hydrogen molecule (H2)
- Chlorine molecule (Cl2)
- Hydrogen fluoride (HF) molecule
- Water molecule (H2OR)
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) molecule

Examples of double covalent bond
- Oxygen molecule (O2)
- Carbon dioxide molecule (CO2)
- Ethylene molecule (C2H4)
- Propylene molecule (C3H6)
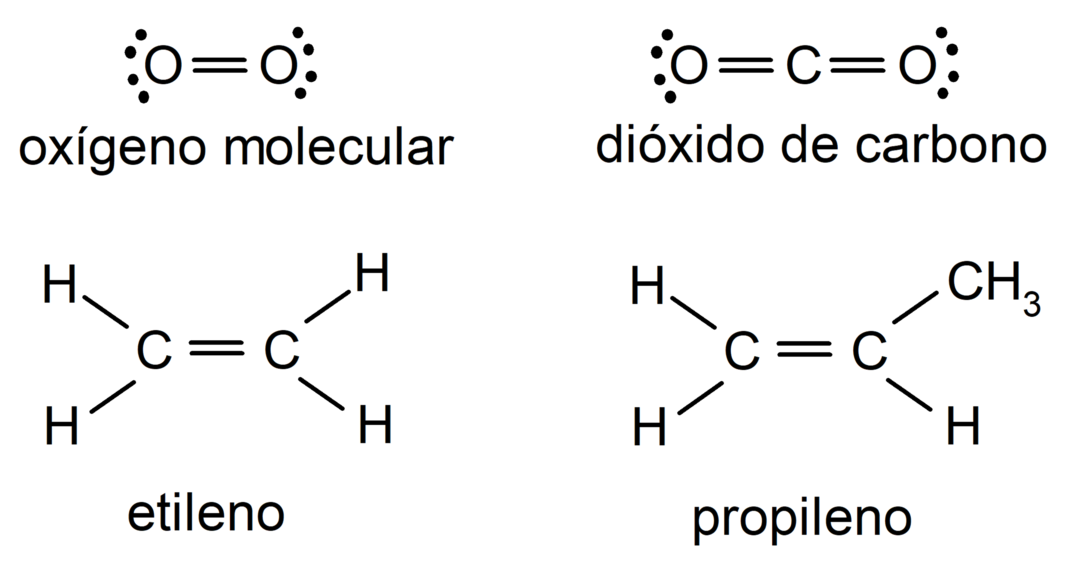
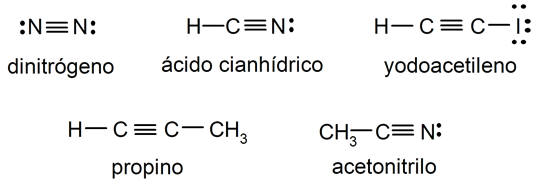
Examples of triple covalent bond
- Nitrogen molecule (N2)
- Hydrogen cyanide (HCN) molecule
- Iodoacetylene molecule (HC2I)
- Propine molecule (C3H4)
- Acetonitrile molecule (CH3CN)
Follow with:



