20 Examples of Acids
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
The acids make up an important group of chemical compounds, very wide. Acids are generally defined as compounds that can donate one or more cations hydrogen (H+) to another compound, known as base. Although in reality, acids are defined according to several theories:
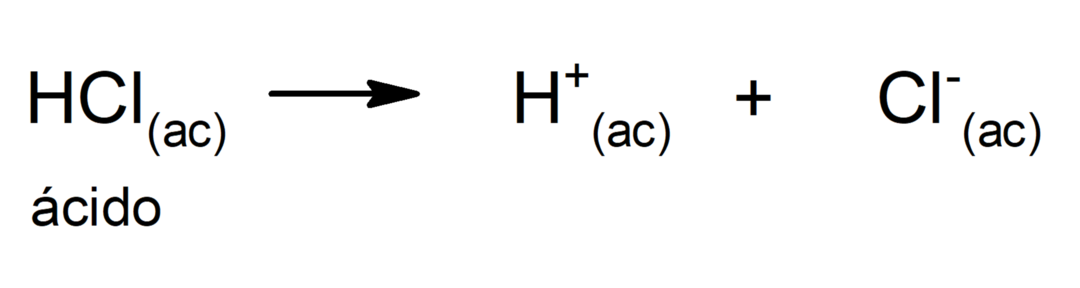 The limitation of this theory is that acids are defined only in aqueous solution.
The limitation of this theory is that acids are defined only in aqueous solution. 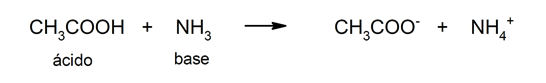

The property of releasing hydrogen cations is what makes acids produce solutions of pH less than 7. Acids that can release more than one proton (using this name for H+) are called polyprotic or polyfunctional.
Acid properties
Regarding their properties, acids can be presented as liquids or as gases, more rarely as solid. The acid taste that we can recognize and that characterizes these compounds, we find, for example, in citrus fruits, which are rich in citric acid, or vinegar, which is an acid solution acetic. These are organic acids.
exist organic and inorganic acids; the strongest are usually the inorganic ones. Many organic acids serve important biological roles. Among the inorganic ones there is one, hydrochloric acid, which plays a very important role in the digestion process. The
nucleic acids They are also fundamental for life, as they are the basis of the genetic material of the cells and contain the key to the synthesis of protein.The tendency to lose protons is what determines the strength of an acid.
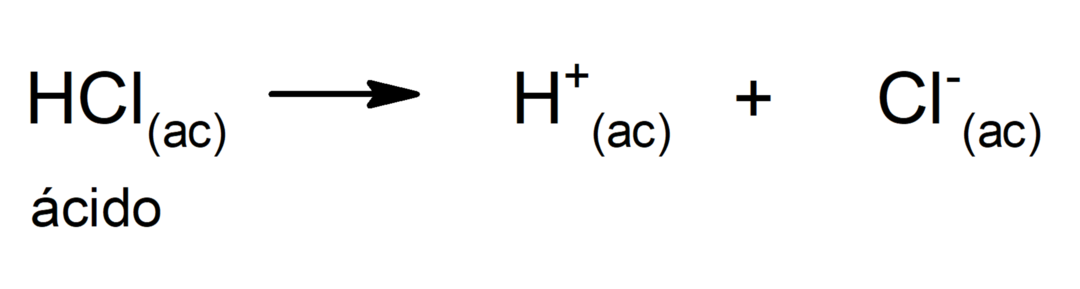
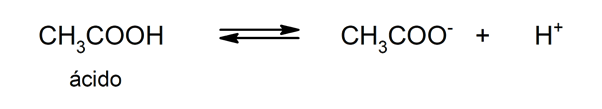
Uses of acids
Acids have many uses, both on an industrial and home scale. They are often used as additives and preservatives in food, cosmetics, beverages, etc. Some acidic solids are used as catalysts (chemical reaction accelerators) in the petrochemical or paper industry.
There are also acids that are used as disinfectants (carbolic acid, salicylic acid). In addition, they can be used as electrolytes in car batteries, as is the case with sulfuric acid. The latter strong acid is also frequently used in the processing of mineralsSuch is the case of the production of fertilizers from rock phosphates.
It is worth clarifying that certain substances can only be solubilized in acidic media, and that certain reactions only occur under such conditions. Nitric acid and ammonia make ammonium nitrate, also an important fertilizer for crops.
Examples of acids
Twenty acids are listed below, by way of example:
- Perchloric acid (HClO4). It is a strong acid liquid a temperature environment, highly oxidizing.
- Nitric acid (HNO3). It is a strong and intensely oxidizing acid, used to make certain explosives and also nitrogen fertilizers.
- Ascorbic acid (C6H8OR6). It is vitamin C, so necessary for health. It is a protective substance for its antioxidant effects.
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl(ac)). It is the only strong acid that the human body synthesizes, a process that specifically occurs in the stomach to carry out the degradation of the food in the digestive process.
- Tartaric acid (C4H6OR6). It is a white crystalline powder, it is used in the preparation of effervescent drinks, in the bakery, wine and pharmaceutical industries. The cream of tartar that some recipes carry is tartaric acid.
- Hydrofluoric acid (HF(ac)). Because of its ability to attack glass, it is used in crystal carving and engraving.
- Sulfuric acid (H2SW4). It is a strong acid par excellence, it has countless applications in various industries and synthesis processes.
- Trifluoroacetic acid (C2HF3OR2). It is a good solvent for many organic compounds.
- Phosphoric acid (H3PO4). It is present (in low concentrations) in various cola drinks. It is considered harmful to health as it promotes decalcification.
- Acetic acid (CH3COOH). It is the main component of vinegar. The acidity it creates makes it a widely used food preservative.
- Fluoroantimonic acid (SbHF6). It is the strongest known superacid, exceeding the acidity of pure sulfuric acid by 1019.
- Chromic acid (H2CrO4). It is a dark red powder, it participates in the chrome plating process. It is also used to glaze ceramics.
- Indoleacetic acid (C10H9NOT2). It is the main representative of auxins, important in growth hormones of plants.
- Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). It is the one that holds the key to life, since it makes up the genes that govern the synthesis of countless proteins.
- Tricarboxylic acids. They comprise a group of carboxylic acids that have three carboxylic groups (-COOH). Citric acid (C6H8OR7) It is one of them.
- Formic acid (CH2OR2). It is the simplest of the organic acids. Prolonged exposure to this acid can cause respiratory failure and death.
- Gluconic acid (C6H12OR7). The salts of this acid are widely used in glassware cleaning processes.
- Lactic acid (C3H6OR3). It is an important part of biochemical processes.
- Benzoic acid (C7H6OR2). It is an acid with a characteristic odor that is widely used to preserve foods that require a pH acid.
- Malic acid (C4H6OR5). It is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry to produce laxatives.
- Carbonic acid (H2CO3). In some places it is part of the process of formation of the caves. It is present in carbonated drinks.
