Concept in Definition ABC
Miscellanea / / September 13, 2021
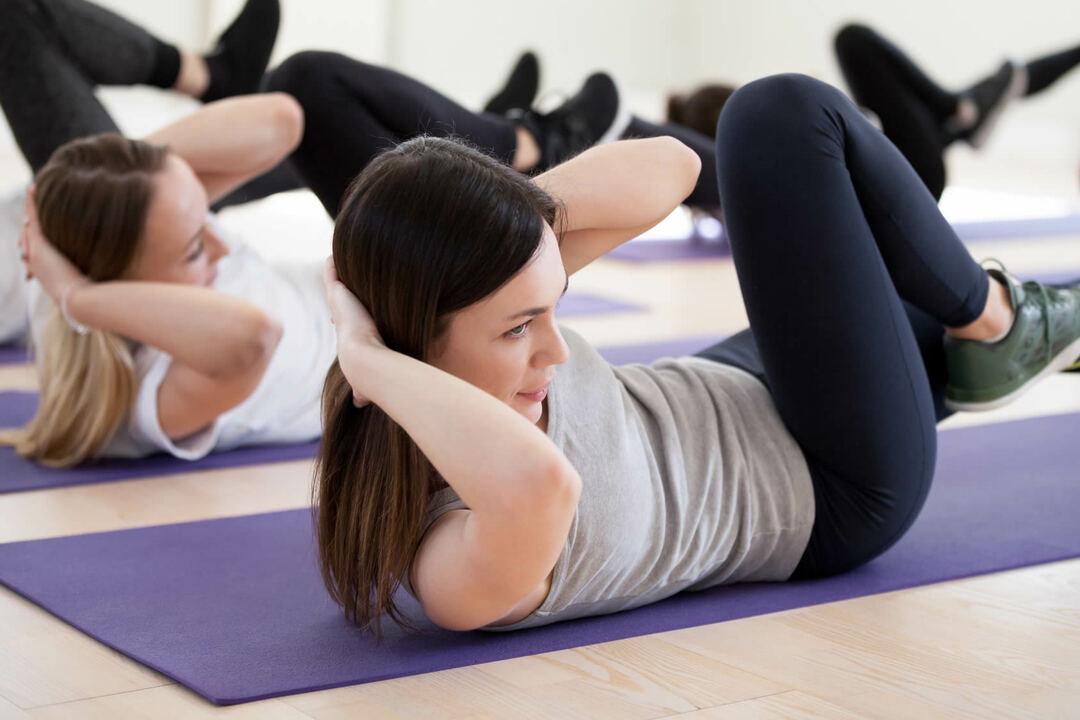 The core describes the muscle formation present in the lumbopelvic area, as the central point of the trunk, built by 58 muscles that are distributed bilaterally at the level of the lower back, pelvis, hip and wall abdominal. This region makes up the body's center of gravity.
The core describes the muscle formation present in the lumbopelvic area, as the central point of the trunk, built by 58 muscles that are distributed bilaterally at the level of the lower back, pelvis, hip and wall abdominal. This region makes up the body's center of gravity.
This interpretation at the physical level it arises from the business and business, on the idea of the main center on and from which one works. Starting from identifying and establishing the core, grouping the points that stand out in the company, strategies are put into practice, and the general organization of the human Resources, operating and investment expenses in order to advance on clear objectives.
Muscle groups that make it up
Abdomen. Integrated by the rectus, transverse and oblique of the abdomen. These are located in the anterior and lateral part of the trunk. Their function is to contain and protect the organs and other structures located within the abdominal cavity. They are also involved in the process of breathing.
Lumbar region. Here are grouped various muscle masses involved in the adoption and maintenance of the upright posture as well as in the movements of flexion, extension, rotation and lateral flexion.
Pelvis and hip. This region is particularly important for ambulation, it encompasses the muscles of the pelvic floor, the gluteal region and the psoas. iliac that is inserted anteriorly in the femur and posteriorly in the lumbar vertebrae, allowing it to act as a flexor of the hips.
These structures make up the so-called active subsystem, which is endowed with the ability to movement. However, this requires the support and support of a passive subsystem formed by bones, ligaments, cartilage, intervertebral discs and joint capsule, which provides it with points of insertion to the various elements of the active system.
Stabilization of the trunk is essential in some sports practices
Movement patterns begin at the core level and are subsequently transmitted to secondary muscle groups, such as those located in the limbs, where the proper distribution of forces towards the arms and legs is accompanied by the need to stabilize the region to maintain the Balance during the execution of the movements.
An example of this is the stabilization of the middle part of the body necessary during activities that warrant twisting, such as when taking a serve during a game of tennis or kicking a ball in the soccer.
Benefits of achieving greater core motor control
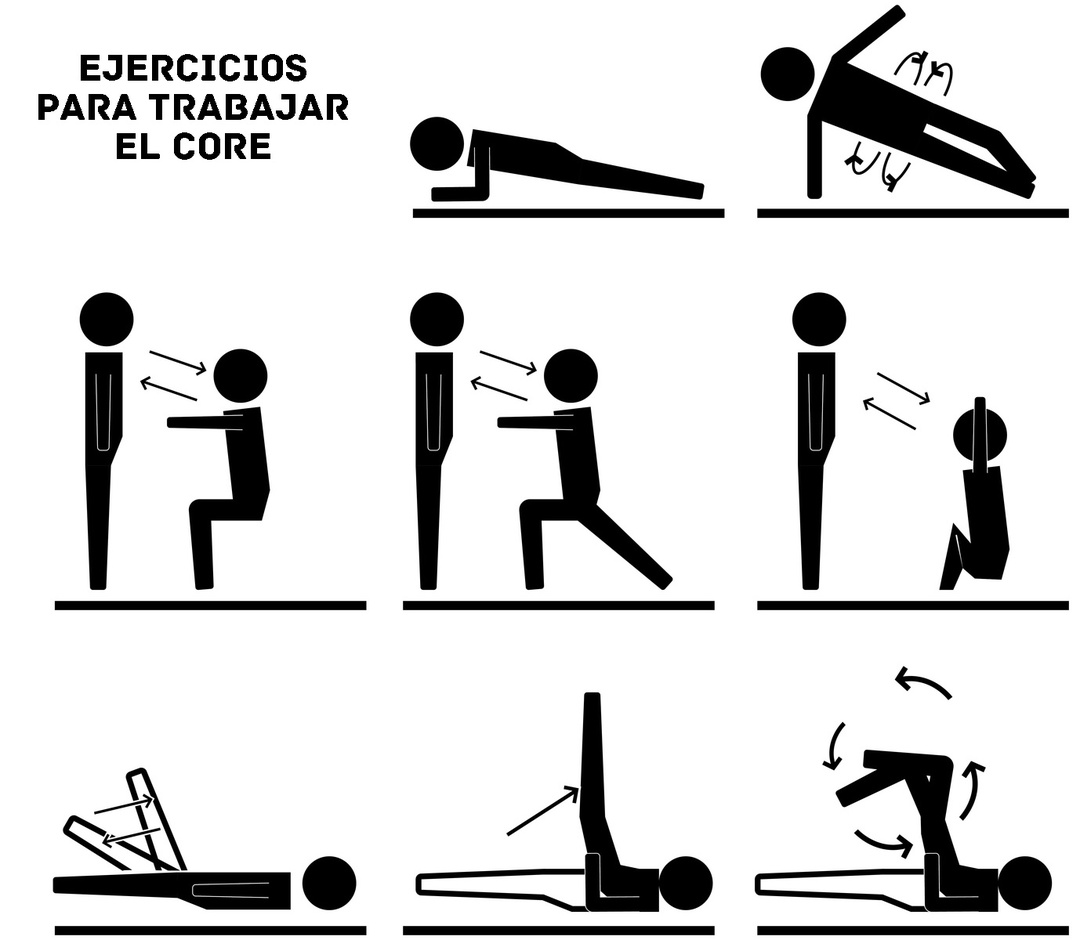 In addition to allowing greater stability and balance of the trunk, the adequate strengthening of the various blueprints muscles of the abdomen, back, pelvis and hips, offers a lot of benefits. These include:
In addition to allowing greater stability and balance of the trunk, the adequate strengthening of the various blueprints muscles of the abdomen, back, pelvis and hips, offers a lot of benefits. These include:
- Prevents the development of injuries due to biomechanical imbalances.
- Contributes to a faster recovery after exercise, especially in sports such as cycling.
- Allows a better alignment of the lower limbs which provides greater resistance against the development of knee injuries.
- Delays the recovery time from various types of injuries, especially those of sports origin.
- Helps to improve, and even eliminate, back pain related to injuries such as herniated discs.
- It allows to have a greater performance, since it reduces the work that must be done by the peripheral muscle groups.
Photos: Fotolia - fizkes / cbproject
Topics in Core


