20 Examples of Gaseous State
Miscellanea / / November 13, 2021
In general, when talking about States of the material reference is made to three large groups: solid, liquid and gaseous (although there is also the plasma state).
The gases They are a state of the matter in which the molecules interact weakly at certain temperature and pressure. For example: biogas, carbon monoxide, hydrogen, methane.
In the gaseous state, the molecules are not cohesive, so gases do not constitute a consistent body, with a defined shape and volume, as solids do. For this reason, gases are often imperceptible to vision, although some are perceptible to smell.
The gases expand throughout the available space, that is, they adopt the shape and volume of the container that contains them.
State changes:

Characteristic of gases
Research on gases and air
There are many studies and theoretical contributions on physics and chemistry to analyze the characteristics and behavior of gases.
The air (that almost all living beings we need to breathe) must have a certain composition, with a sufficient amount of oxygen. Carbon dioxide is also an important gas in the air,
plants They need it to carry out the photosynthesis process.Certain gases should not exceed a certain proportion in the air; in fact some gases from certain industries are extremely toxic and harmful to health, and can pollute the atmosphere we breathe (the carbon monoxide is an example of them).

Gas properties
Among the main properties of gases, we find:
The behavior of gases was described through the Gas laws formulated by scientists like Robert Boyle, Jacques Charles, and Gay-Lussac. These physicists related parameters such as volume, pressure and temperature of the gases, which are gathered in the so-called General gas law.
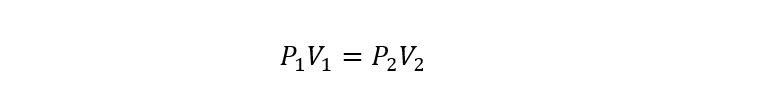
Where:
P1 Y P2 are the initial and final pressures of the gas respectively.
V1 Y V2 are the initial and final volumes of the gas respectively.
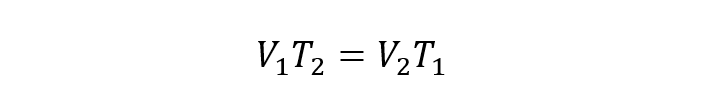
Where:
T1 Y T2 are the initial and final temperatures of the gas respectively.
V1 Y V2 are the initial and final volumes of the gas respectively.

Where:
T1 Y T2 are the initial and final temperatures of the gas respectively.
V1 Y V2 are the initial and final volumes of the gas respectively.
Examples of matter in a gaseous state
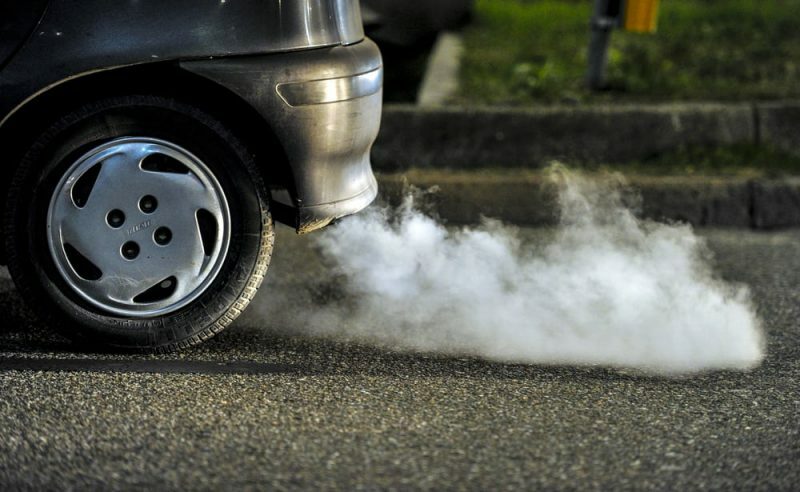

- Emissions coming out of the tailpipe of a moving car.
- The gases used in the refrigeration of refrigerators and air conditioners.
- The clouds in the sky, composed of water vapor.
- Carbon dioxide in carbonated drinks.
- Tear gas, which produces an unpleasant sensation on the human body.
- Gas balloons (filled with helium gas).
- Natural gas used as fuel in the home network.
- Biogas.
- The smoke that is generated when burning any solid.

- Carbon monoxide
- Acetylene
- Hydrogen
- Methane
- Butane
- Ozone
- Oxygen
- Nitrogen
- Hydrogen sulfide gas
- Helium
- Argon



