Definition of electrical charge
Miscellanea / / November 13, 2021
By Florencia Ucha, in Sep. 2010
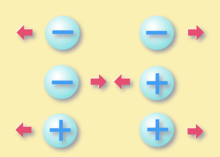 At the request of the Physical the electric charge turns out to be a property intrinsic that some subatomic particles present which will manifest itself through attractions and repulsions which will determine the electromagnetic interactions between them, being the same positive charges and charges negative.
At the request of the Physical the electric charge turns out to be a property intrinsic that some subatomic particles present which will manifest itself through attractions and repulsions which will determine the electromagnetic interactions between them, being the same positive charges and charges negative.
Electrically charged matter will be influenced by electromagnetic fields at the same time it generates them.
The interaction between charge and electric field will give rise to one of the four fundamental interactions which is the electromagnetic interaction.
Historically, electrons, quarks and protons they were assigned different charges, for example, electrons present negative charge -1, also known as -e; on the other hand, the protons have a charge positive +1 or also + e, meanwhile, to the quarks they were assigned a fractional charge.
According to what the System International Of units the electric charge is called coulomb (c) and defines it as that amount of load that passes through the section
cross of a certain electrical conductor during the span of a second and when the electric current is from a amp.The nature of the electrical charge is discrete.
Already from ancient Greece the property of attraction of light bodies that show some materials, meanwhile, it would be only in the middle of the XIX century when all the observations obtained from Ancient Greece would be formally systematized.
Topics in Electrical Charge