Definition of Atomic Structure
Miscellanea / / January 13, 2022
concept definition
It is the way an atom is made up. When we speak of atoms, we refer to the smallest particles that can retain the properties of a certain element.

Chemical engineer
According to Periodic table, there are approximately 118 different kinds of atoms that, when grouped together, form molecules. The structure of the atom was studied by different scientists until reaching what we now take as a criterion. general, which is that an atom is made up of two well-differentiated zones: the nuclear zone and the extra zone nuclear.
The nuclear zone is formed by the positive charge (protons) and neutral charges (neutrons), which is why it makes up almost 99.99% of the atomic mass despite having a reduced size of 10-12 cm. The particles inside are held together by nuclear forces, very strong forces that give rise to Nuclear energy.
Despite having the lowest atomic mass, the extranuclear zone occupies 99.99% of the volume of the atom, and it is negatively charged being the host zone for electrons, which are in continuous movement indefinitely.
When the atom is neutral, the number of electrons and protons are said to be equal. Now, when an atom loses or gains electrons, remaining positively or negatively charged, ionic species called cations and anions are formed. Depending on the number of electrons gained or lost, they are assigned a name, for example, in the case of Aluminum, which is a metal that forms a positive ion, since it loses three electrons, it is called a trivalent cation.
If we look at the masses of the subatomic particles we would see that they are similar in the order of the protons and neutrons while electrons have a lower mass, all of them defined in the Periodic Table in the Unit of "uma". "uma" means "Atomic Mass Unit" and is defined as one twelfth of the atomic mass of carbon, to establish a reference magnitude. In turn, it is defined as the following equivalence:
1 amu = 1.66 x 10-24 grams
If we look at the orders of magnitude, they realize that it is a tiny and imperceptible value to human vision. So when reading the atomic mass of an element, for example, in the case of Helium we see that it is 4.002602 amu or, what is the same, 6.64x10-24 grams.
When defining the atomic structure of an element we refer to two known numbers that allow us to quickly identify the atom we are naming. These numbers are: the atomic number and the mass number.
The atomic number or "Z" represents the number of protons that the atom has in its nucleus. As we said before, if the atom is neutral, "Z" also corresponds to the number of electrons in the extra nuclear zone. Thanks to its number "Z" we can locate it in the Periodic Table, which will give it a series of certain properties. As for the mass number or "A" it refers to the number of protons and neutrons that the atom has in its nucleus. In general, both numbers are expressed as follows:
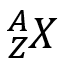
Where X represents the symbol of chemical element.
Although for a certain “X”, “Z” is unique, “A” can vary due to the existence of isotopes.
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons. Therefore, they may have the same "Z", that is, the same number of protons, but not the same "A" since the neutrons vary from one to another.
There are many examples of isotopes in nature, the most widespread are the isotopes of Carbon. There are the following atomic structures for the same element:
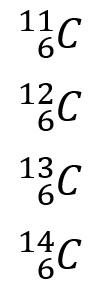
As we can see, in each of them, the number of neutrons varies. All species conserve six protons while the first has 5 neutrons, the second 6, the third 7 and the last 8. Depending on the isotope is that the use is determined. For example, the isotope Carbon-13 is the least available in nature despite being physically stable. Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope with applications in this field and graphite is one of the most useful isotopes today.
Topics in Atomic Structure


