Definition of Mediation and Moderation (in Statistics)
Inhibition String Theory / / April 02, 2023

PhD in Psychology
Set of multivariate techniques in which the "how" in a relationship between an independent variable (X) and a variable is investigated. dependent variable (Y), which is done by including a third variable (or more than one) that can take the role of mediator or moderator.
Mediation
Imagine that a investigation has the objective of determining how the exposure weighty ideals manifested in the media communication influences dissatisfaction with the body. The people responsible for the research have hypothesized that the internalization of the rule around thinness turns out to be a relationship mediator.
The mechanisms through which a variable X influences a variable AND. In other words, that any variation in X will cause changes in one or more mediating variables (m) and this in turn will cause changes in Y. Graphically the simplest model of mediation is the following.
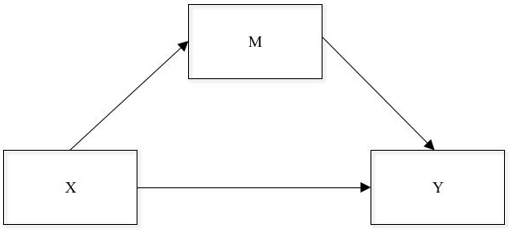
The researchers who use this technique estimate and test hypothesis from two types of effects or relationships (they can also be found under the name of
pathways Or simply paths).1. direct effects. Refers to the direct relationship between two variables, either X ⟶ Y or X ⟶ M
2. indirect effects. It refers to any effect that passes through a mediator. X ⟶ M ⟶ Y
Once both effects have been estimated, the following question remains to be resolved: is the mediation partial or total?
• partial mediation. It happens when the direct effect of X about AND it remains statistically significant in the presence of a mediator.
• full mediation. It happens when the direct effect of X about AND it ceases to be statistically significant in the presence of a mediator.
In the example above, weight ideals alone cause dissatisfaction. bodily in some people, however, these ideals cause the norm around weight to be internalized, which also generates body dissatisfaction.
Moderation
An investigation aims to determine what factors cause negative beliefs about vaccines to reduce vaccination intention. The people responsible for the research hypothesize that exposure to false information increases the effect of these beliefs. How could they test this hypothesis?
In moderation, the objective is to determine the condition of the relationship between a variable X and a variable Y. This condition is studied by inclusion of a moderator variable (W), which influences the size or valence of the relationship between X and AND. That is, the inclusion of W can strengthen the relationship or turn it negative if it is positive. It is also possible to find this relationship with the name of interaction effect. The simplest form of moderation can be visualized in the following diagram.
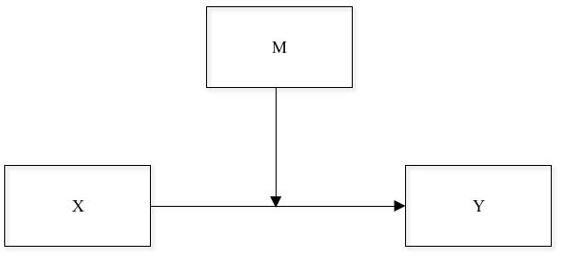
When testing hypotheses based on this technique, one must first determine the linear interaction between X and W in relation to Y If such an interaction is significant, the nature of the association should be described by estimating the relationship between X and Y at different values of W.
In the example above, people who have negative beliefs about vaccines have low vaccination intention; and when they receive false information about the side effects of the vaccine, the effect of the beliefs becomes even greater.
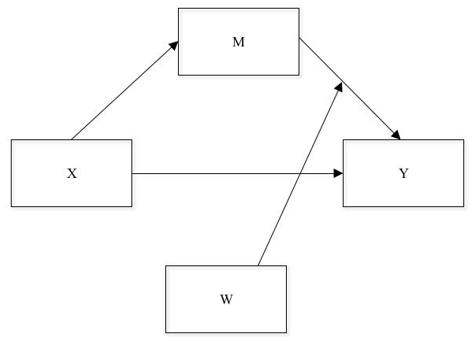
Moderated mediation (conditional process)
Although research based on the inclusion of a third variable usually addresses mediation or moderation as techniques applied separately, it is also possible to apply them simultaneously in the same model. This last proposal is less common, however, ignorance of this technique is understandable; since moderated mediation, also known as conditional process, has not been developed for more than 20 years. This has caused that there is still no consensus among researchers regarding which are the appropriate analysis techniques for this process. Even the name is still under discussion (it has been called moderated mediation, mediated moderation, and conditional process).
Beyond the discussion around the name and the analysis techniques used, it should be understood that moderated mediation or conditional process occurs when a moderator variable interacts with a mediator variable in such a way that the effects indirect (X ⟶ M ⟶ Y) are modified by the values of the moderator variable. Visually, this relationship would look like this: