Rod Pump Definition
Reliability Electric Resistance / / April 02, 2023

Chemical engineer
The rod pump is the pumping unit in charge, through the crankshaft - connecting rod - piston system of the extraction of crude oil in a perforation, easily identifiable when circulating in areas close to deposits oil.
Depending on the type of well being exploited, additional help is often required to lift the fluid to the surface. Thus, there are wells, called springing whose fluid has enough pressure to go to the surface, while others require the delivery of additional mechanical energy, whose device in charge of this purpose is the "stork", as this device is popularly called. system.
Operating principle
Although the rod pump, today, is the most widely used equipment in oil drilling, it turned out to arise from a combination of two mechanisms that acted separately for the same purpose. On the one hand, there were the "Horseheads" and, on the other, the "Air Balances". The "horseheads" or horse heads have a rocker and a pivot in their center. The drilling rod is located at one end while the counterweights are located at the other, which are two steel beams. When a crank rotates the counterweight, the rocker moves down and the beam allows the displacement of the rod in a certain period, allowing the oil to rise towards the surface. On the other hand, the "air balance" or air balance has the pivot at the end of the rocker arm and not in its center, when the drill rod descends helps the compression of the air inside a cylinder and the pressure exerted by this compressible fluid causes the rocker arm to rise and extract The crude.
The combination of both mechanisms gave rise to the rod pumps. These pumps are attached to a motor, generally electric, which provides the necessary energy to move a system. of pulleys, in counterweight, these pulleys transmit the movement to a connecting rod that constantly raises and lowers a crank. At the other end, there is the "horse's head", from which a metallic cable or steel cable is attached at its end to a polished rod. Through a system of gears and steel bars that reach the bottom of the pipe designed for extraction, at the bottom of the pipe The pump is located together with its piston, which allows the pumping of the liquid towards the surface, this liquid being mostly water and hydrocarbons.
Depending on the type of well, its pressure and the composition of the mixture, the amount of crude oil and water to be extracted and the size of the pumping unit that will be necessary are determined.
The equipment and its parts is a relatively complex system with a simple drive principle, as can be seen below for each of the mentioned parts:
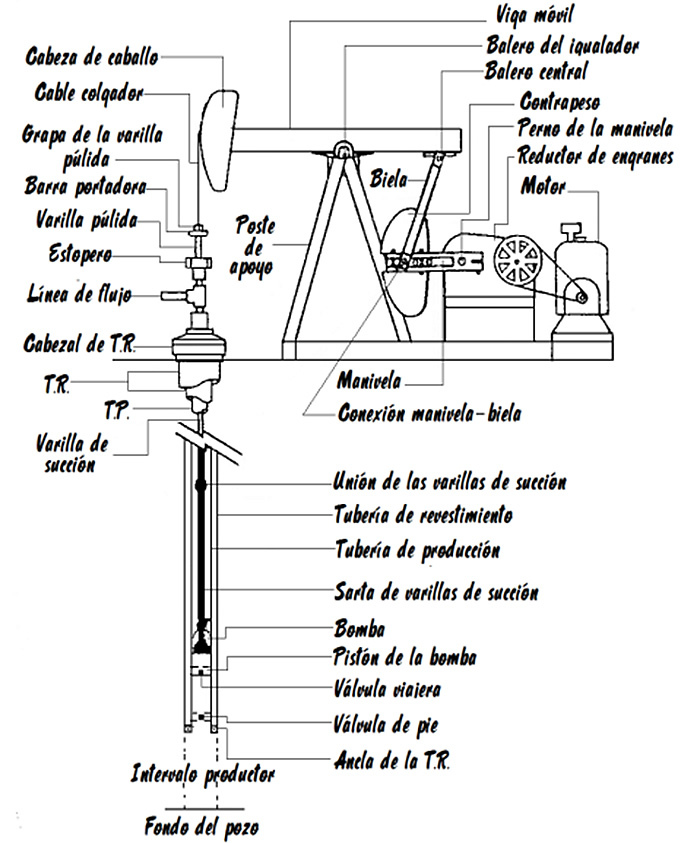
As for the pump located at the bottom of the well, it is also known as a subsurface pump and is a positive displacement pump, that is, it delivers a constant flow regardless of the pressure. This pump consists of two valves: a fixed valve or "foot valve" and a mobile valve that moves together with the piston which, in turn, as seen in the photo, is connected to the rod string of suction. In the coordination of the movement, when the string rises, the mobile valve closes and the immobile valve opens, here the pump cylinder is filled with the mixture of fluids, ascending by the drive of the piston. As the rod string descends, the traveling valve opens while the stationary valve closes, thus mixing Hydrocarbon water sucked by the piston in its upward movement flows towards the surface through the valve mobile. When the piston moves back, another cycle begins again.
Many drilling fluids are triphasic, that is, a certain gas content is added to the previous mixture, if this gas is compressed in the cylinder, the necessary pressure for valve opening is not reached, lowering the pumping efficiency and giving rise to possible cavitations. For this reason, when the existence of a triphasic fluid is known, the gas is previously bubbled through the annular zone that is designed in the production piping system and, in this way, the entry of gas to the unit is avoided. pumping. Depending on the amount of gas extracted, it can be used for sale as natural gas, post-treatment, or it can be reinjected into the pumping system as fuel.