Respiratory System Definition
Pet Scan Speciation Blood Type / / July 28, 2023

Lic. in biology
The main function of the respiratory system is to bring air or water from the environment into the body and put it in contact with the blood. Contact occurs on a thin layer of tissue that is always moist and full of blood vessels. This layer of tissue is called the respiratory surface, and it is there that gas exchange occurs. The blood has proteins designed to capture oxygen when exposed to air or water that contains this gas. When these proteins have captured oxygen, the blood is said to have become oxygenated.
Another important function of the respiratory systems is to expel carbon dioxide out of the body, which is waste. This gas goes the opposite way to oxygen. It reaches the respiratory surface through the circulatory system, and from there it passes into the air or water. This is the excretory function of the respiratory system.
 One of the fundamental activities for the life of all living beings is the cellular respiration, which is the chemical reaction by which cells obtain energy from carbohydrates in the diet
One of the fundamental activities for the life of all living beings is the cellular respiration, which is the chemical reaction by which cells obtain energy from carbohydrates in the diet
Types of respiratory systems
Breathing in animals has adapted to different ways of life, and even to different environments. Thus, there are respiratory systems useful for extracting oxygen from water and others for breathing air.
In the skin respiration, the respiratory surface is the body's own skin. This type of respiration occurs in some aquatic and terrestrial invertebrate animals, such as sponges, jellyfish, and earthworms. Some amphibian vertebrates also have this type of respiration, although in vertebrates, the main respiratory organs are the lungs.
The advantage of this type of breathing is that it does not require specialized organs, but the disadvantage is that it is only efficient in small animals and that the skin must always be moist to function as a surface respiratory. If the skin dries out, the animal dies from suffocation.. This happens, for example, with earthworms, which die when exposed to the sun because their skin dries up and they can no longer breathe.
Cutaneous respiration is useful both in air and in water.
The gill breathing is typical of aquatic animals, such as fish, octopus and squid, and tadpoles (the larvae of amphibians). Gas exchange occurs in sheet- or hair-shaped structures called gills, which are in contact with water.
The advantage of gills is that they allow the oxygen dissolved in the water to be used, but the disadvantage is that they are delicate and can be easily damaged. They only work in water, and any animal with gills is incapable of breathing air..
The tracheal breathing It consists of the exchange of gases through tubes called tracheas, which communicate with the outside through holes called spiracles. It is like a long branching pipe that carries air into the body.
This type of breathing occurs in the insects and some arachnids. In other terrestrial arthropods, respiration occurs through book lungs, which are like bags or air sacs open to the outside. Inside the sac, there are partitions through which the hemolymph circulates so that it is oxygenated. Aquatic arthropods breathe through gills..
The advantage of tracheal breathing is that it allows air to be brought directly to the cells, without rely on the circulatory system, but the downside is that it limits the size and activity of the animals. An animal with tracheas cannot be very large, otherwise the network of tubes would have to be immense and would occupy a large part of its body.
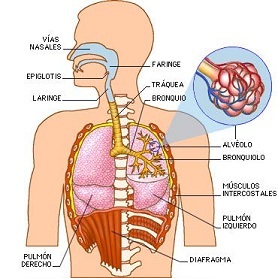
The lung breathing, which is adult amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals, consists of the exchange of gases through organs called lungs. Air is carried to the lungs through a tube called the trachea.
In mammals there are two lungs. Birds have air sacs that allow them to store air and facilitate its continuous flow through the lungs.
Unlike other vertebrates, which fill their lungs when they inhale and empty them when they exhale, birds fill their lungs when they inhale, but also the air sacs. That air is "stored" in the bag. When the bird exhales, the lungs are emptied, but the air that was stored in the air sacs fills the lungs again.
Thus the bird always has its lungs full of fresh air (air with oxygen). This continuous flow of fresh air into the lungs helps them keep the oxygenation of the blood high to maintain a high metabolic rate (flying takes much more energy than swimming or walking). 0
In addition, birds have the problem that the amount of oxygen in the air decreases with height, so it is necessary to breathe more volume of air to get the same amount of oxygen at high altitudes than at sea level. This is what happens with mountaineers, whose lungs have no adaptations for breathing in height and have to train a lot to improve their physical performance in low oxygenation. The air sacs of birds are an excellent adaptation to improve the efficiency of the lungs..
Fish are the only aquatic vertebrates that can breathe in water. The rest breathe through their lungs, and therefore need to surface in order to breathe air. If they can't get out of the water to breathe, they drown.
Usually, the lungs are located in the center of the body: in the thorax. Therefore, for oxygenated blood to reach the entire body, a complex circulatory system is needed.

