20 Examples of Sugars
Examples / / November 06, 2023
The sugars are the carbohydrates which, in general, have a sweet flavor. The term “sugar” is primarily used to refer to sucrose, which is the common sugar used to sweeten foods and desserts. Some examples of sugars are: glucose and sucrose.
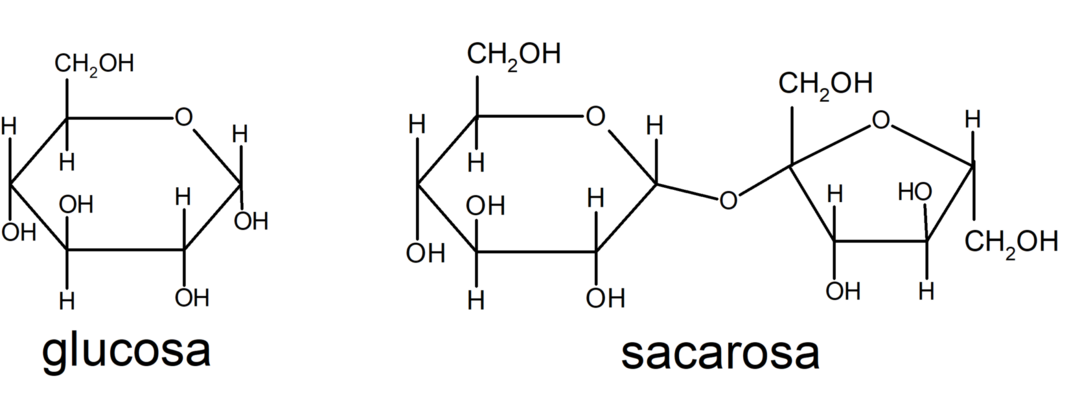
Carbohydrates are molecules made up of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O), although some contain sulfur (S), nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P).
- See also: Monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides
Types of sugars
Sugars are classified according to the number of monomer units that compose them into:
Monosaccharides
Monosaccharides are sugars made up of a single monomer unit, they are the simplest sugars. For example: glucose and fructose.
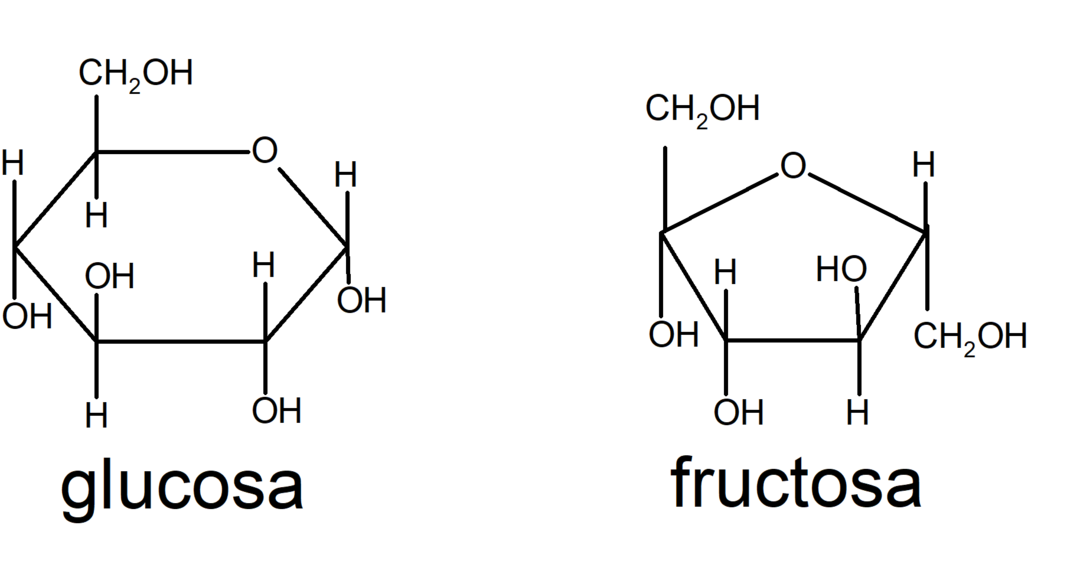
Disaccharides
Disaccharides are sugars made up of two monomer units. For example: sucrose and lactose.
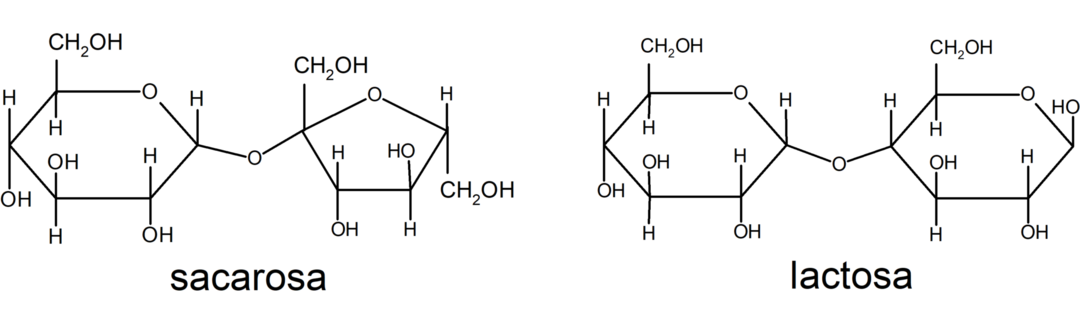
Trisaccharides
Trisaccharides are sugars made up of three monomer units. For example: maltotriose and raffinose.

Biological function of sugars
The main function of sugars in the human body is to provide the energy necessary for the correct functioning of the different organs, mainly the brain and muscles.
The brain alone consumes approximately 20% of the energy that comes from glucose. Furthermore, glucose is the source of energy used by all tissues in the body.
When glucose levels in the human body are very low, certain problems begin to appear such as weakness, tremors, mental confusion and fainting.
Added sugars
Sugars can be found naturally in food or they can also be added as part of the production or preparation process. Added sugars are those that are added to foods.
Added sugars provide foods with a high caloric level, but low nutritional value. Incorporating too much sugar in the diet can affect health, causing type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Many beverages, such as sports drinks, processed fruit juices, energy drinks, and Regular soft drinks contain a high level of added sugars, so it is recommended to limit their consumption.
Examples of sugars
- glucose
- ribose
- mannose
- fructose
- galactose
- saccharose
- lactose
- mannose
- trehalose
- maltotriose
- raffinose
- maltose


References
- Cabezas-Zabala, C. C., Hernández-Torres, B. C., & Vargas-Zárate, M. (2016). Sugars added to foods: health effects and global regulation. Literature review. Journal of the Faculty of Medicine, 64(2), 319-329.
- Gómez Morales, L., Beltrán Romero, L. M., & García Puig, J. (2013). Sugar and cardiovascular diseases. Hospital Nutrition, 28, 88-94.
- Pellerin, P., & Cabanis, J. c. (2000). The carbohydrates. In Oenology: Scientific and technological foundations (pp. 66-96). Mundi Press Books.
Follow with:
- Carbohydrates (and their function)
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
