Education Features
Basic Knowledge / / July 04, 2021
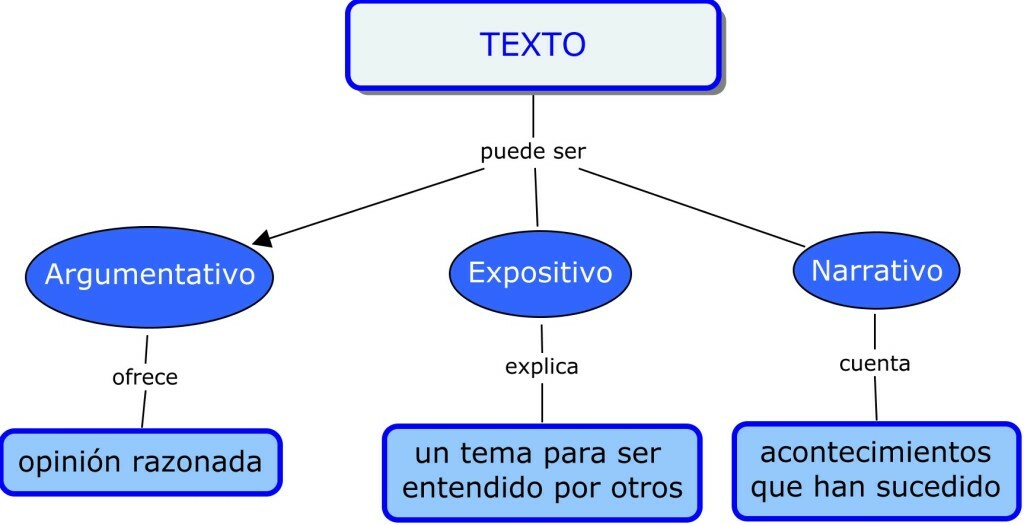
Education is called the various processes that an individual receives and that are focused on stimulating the learning of new information, as well as influencing cognitive development and physical nature of a person, and that is generally focused on a pre-established trend, (religious education, civic education, etc.), but aimed at training individuals to face the challenges that daily life imposes, as well as to promote and develop the inventiveness of the person, transmitting knowledge, values, cultural traditions, as well as ways of Act. The word education derives from the Latin word "Educare", what did it mean to guide or lead, understanding also how to train and instruct.
It is also known as education, the various rules of civility and courtesy that are instilled in people to function in social life.
Some types of divisions of education:
They can be divided into two main branches:
- Traditional education
- Schooled education
It can also be divided by taking other parameters, such as the subject it is focused on:
- Religious education
- Traditional
- Military
- Scientist
- Ate
- Nationalist
- Physical
Or by the school level to which it is directed:
- Preschool or initial education (Kindergarten or Kindergarten)
- Primary education
- Secondary education
- Middle-higher education
- Higher education (university and postgraduate).

Some of the Characteristics of Education:
Generally, when the word education is used, it refers to the so-called “formal education”, that is, it refers to the various educational processes carried out by teachers, who They are aimed at fostering the intellectual capacities of students, as well as the learning of knowledge and the inculcation of values tending that the person who is being Educating learns the knowledge and social, labor and intellectual behaviors, appropriate to function in daily life, using for this the tools provided by the pedagogy. This type of education has been systematized during the 19th and 20th centuries, being quite standardized in some of its processes, although at present there have been large changes in the systems used, thanks to new tools such as computers, internet, television and other technological implements used to help the process educational.
Education Division.- Education can be divided into different ways, depending on the line of thought or the approach in which it is developed, and can be done for example, by trends religious or scientific, or be directed towards a specific purpose, as may be the case of military education, which combines discipline, technical knowledge and physical exercises, and in the same way the parameters of education change, by changing the approach to which it is intended, as in the case of medical education, sports, etc. But usually education is divided into two main branches, which are traditional education and school education, these in turn are subdivided either by the type of themes that are instilled in the person, the fields they cover or by the type of systems and tools used for the teaching. For example, traditional education focuses on issues related to social behavior, religious themes, or traditional customs typical of a certain population, etc. While school-based education tends to be more universal in the subjects it teaches and has systematized methods, as well as that in school-based education there are both basic and secondary education and higher education, obtaining sufficient knowledge to carry out jobs that require a specialization, such as medicine, psychology or the same teaching.
Learning.- Learning a variety of knowledge and techniques is one of the goals of education; Through the learning process, knowledge, values and behaviors and various skills are acquired, as well as skills are acquired and modified.
Induction, trial and error.- Among the forms used in education are trial and error processes, which exist among the manifestations that lead to learning.
Evaluations or exams.- In school education systems, to assess the degree of knowledge acquired by students students and the quality of that knowledge, evaluations or examinations are continually end.
Ways to educate.- The oral or written word is the most common way of imparting education, being used for the student to obtain information orally or visually, as well as to receive instructions and indications regarding some type of task to be carried out or a type of teaching material that must be be used.
Various audiovisual materials are also used for the delivery of education, such as books that are read by schoolchildren, as well as videos that are used in schools for certain subjects. In addition to the use of the word, education can be carried out through various attitudes or actions, with which the person can learn, such as the case, for example of physical education, where much of what is intended to be taught by the teacher or coach, is through examples, in which the educator takes positions or attitudes that the learner must imitate, to carry out a certain exercise or movement sports.
Initial education.- The initial or preschool education (kindergarten or simply Kindergarten), is the education that is imparted to young children (between 3 and five years of age), to introduce them to the school education system, its main function being to encourage the child's cognitive and psychomotor processes, encourage verbal communication of the infant, enhance her imagination, and introduce children to social life with other infants of the same age.
Family education.- "Family" education are those knowledge and values that are introduced into the mind of the infant by the members of a family, tending to introduce the child to daily and “local” life, inculcating religious, moral and cultural values typical of the mediate community to which they are belongs.
Continuing education.- Educational processes are not limited to the so-called "school age", but can cover a lifetime, since human beings have the ability to learn new knowledge even in advanced age, being for this reason that in many countries there are programs to provide education to people older than school age, as well as the fact that that educational institutions such as universities for a long time, offer postgraduate degrees to students who have already completed and finished careers and have a range of age older than the rest of the students, deducing from this that the educational process is not limited to the periods of childhood and youth, but that it occurs throughout the entire life.
It is a human right. Education has been elevated to a human right, with compulsory education, at least in terms of basic education (primary and secondary), in the majority of countries, being taught both in schools belonging to the state, as well as in private educational institutions, (religious schools and private schools lay women). Although it should be noted that in a large part of the cases education is deficient (especially that imparted in schools). state), both due to the use of retrograde educational systems, poor educational programs or ignorance of the educators.