Characteristics of the Eukaryotic Cell
Biology / / July 04, 2021
The eukaryotic cells are the cells that contain a defined nucleus, where its genetic material is contained. The term "eukaryote" is a Hellenism formed by the roots "eu", true, true, and "karyon", which means nucleus or nut, and refers to cells "with true nucleus".
Eukaryotic cells are the most recent in the evolutionary process, and they differ from prokaryotic cells ("pre-nucleus") in that the genetic material: DNA and RNA are found in a defined structure known as the nucleus, while prokaryotes have genetic material dispersed throughout the cytoplasm.
Eukaryotic cells have three well differentiated parts: the membrane, which surrounds it; the cytoplasm, which fills a large part of the cell and where the organelles or organelles function, and the nucleus, where the genetic information of the cell is found.
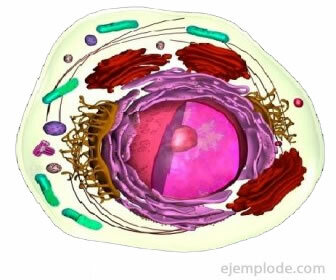
Eukaryotic cells make up unicellular organisms whose cells have a defined cell nucleus, and all multicellular organisms. There are two types of eukaryotic cells: animal and plant. The main difference between them is that eukaryotic animals are heterotrophic cells, that is, that their food is obtained from the outside, while vegetables produce their own food through organelles such as vacuoles and chloroplasts.
Characteristics of the eukaryotic cell:
There are two types:
- Animals
- Vegetables.
Structure of the eukaryotic cella:
Eukaryotes are made up of three main parts:
1.- MEMBRANE:
- Membrane.- The membrane is made up of protein sheets that surround and shape the cell and isolate it from the environment that surrounds it. Through the membrane it can exchange nutrients and oxygen from the medium.
- Cilia and flagella.- They are structures that belong to the menbrane and allow it to move and move in its environment. They are found in many single-celled organisms.
2.- CYTOPLASM:
- Cytoplasm.- The cytoplasm is formed by a liquid medium in which mineral substances, proteins and sugars are dissolved. In this aqueous medium, the chemical reactions that give energy to the cell take place and are also found supporting structures and organelles or organelles, which perform specialized functions within the cell.
Common organelles. Inside the cytoplasm are the organelles that fulfill functions of feeding, respiration and production of substances that the cell needs. There are organelles that are common to both plant and animal cells:
- Endoplasmic reticulum. It is a network of tubes and sacs that are responsible for transporting nutrients through the cell. There are two types of crosshairs: smooth and rough. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is found in cells that produce hormones, in liver cells and in those that are responsible for the metabolism of fats. It is made up of flattened and smooth sacks. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is so named because ribosomes are embedded in its walls.
- Ribosomes. They are the structures in charge of producing proteins, from the RNA fragments that it receives from the cell nucleus. This information also allows them to create long-chain proteins, functions known as protein synthesis.
-
Golgi apparatus. In this organelle, the proteins and fats of the endoplasmic reticulum are combined with sugars (carbohydrates). It also handles cellular waste products that will be secreted out of the cell.
In the cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cell, the organelles are suspended, in these the form and functions are already defined, and in these cells they have their own envelope made of membrane lipid. - Lysosomes. They constitute the digestive system of the cell. In these structures there are several enzymes that are responsible for metabolizing fats, sugars, proteins and nucleic acids, breaking them down into simpler substances that can be used by the cell. They can also break down or neutralize some substances that can be dangerous for cells.
- Mitochondria. With the structures in charge of cellular respiration and energy production. In this organelle, fats and sugars are broken down into simpler substances, releasing energy, which is stored when they combine and form adenosine triphosphate, known as ATP.
- Peroxisome. In animal cells, it is responsible for breaking down hydrogen peroxide (hydrogen peroxide), ethanol and fatty acids into simple substances and energy. In plant cells, it converts lipids into carbohydrates in a state of germination.
- Vacuoles. They are sacks that store water, food and waste materials in the cell. They also serve to regulate the water balance inside the cell. In plant cells they can occupy a large part of their volume, while in animals they are much smaller.
- Cytoskeleton.- This is formed by a series of microscopic supports structured in a three-dimensional way and give the shape to the type of eukaryotic cell in question. They can be microtubules (with a tubular structure) or microfilaments (like small rods of protein).
Animal organelles.
- Centrioles. They produce the microtubules to which DNA binds at the time of cell division. They also form the achromatic spindle during cell division.
Vegetable organelles.
- Chloroplasts: They are responsible for receiving sunlight, through the photosynthesis process, converting light into energy substances such as starch and some amino acids. They are the ones that give the green color to the plants.
- Chromoplasts: with organelles similar to chloroplasts, which also use photosynthesis to transform chemicals for the cell. Some can even synthesize ATP. The chromophyll is the substance found in these structures, and provides various colors to some parts of the plants, mainly flowers, fruits and roots.
3.- CORE
The nucleus consists of 3 structures:
- Nuclear membrane. It separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm. It consists of a series of pores through which it exchanges substances with the cytoplasm and transmits the RNA fragments that make ribosms work.
- Core. The nucleus houses the genetic information in the DNA strands (Deoxyribonucleic Acid), in which it is packaged using proteins called histones, which allow these chains to form small clusters called histosomes.
- Nucleolus A cell can contain one or more nucleoli. In them, RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) is synthesized, responsible for decoding the DNA information and transmitting it to other parts of the cells, such as ribosomes, lysosomes and mitochondria.
