Somatic Cell Example
Biology / / July 04, 2021
The somatic cells are those that make up the tissues of the body, they have complete genetic material and fulfill a specialized function. The cells that make up the human body are generated from the genetic material of both parents, with 23 chromosomes from the father in the sperm, and 23 chromosomes from the mother in the egg. These cells, called germ cells, each contain half the genetic material, and are called haploid. When the egg is fertilized, the resulting cell is a human cell with complete genetic material. All cells with complete chromosomes are called diploid.
During the first days of embryonic development, this cell undergoes a series of divisions by mitosis, in which the genetic material is duplicated, the nucleus is divided and finally two are produced cells. In addition, these cells have the ability to produce any tissue in the body, which is why they are called stem cells.
When these cells are implanted in the uterus, they begin a series of biochemical changes that cause each group of cells to begin to specialize to fulfill a specific function. At this point, human cells go from being stem cells to being somatic cells.
The somatic cells they have a growth and multiplication period called cell proliferation, in which, by the process of mitosis, they duplicate their genetic material, the nucleus divides, and each nucleus ultimately forms two equal cells. However, this process is not infinite, nor does it happen with the same intensity in all parts of an organ. In all tissues there are areas with young cells with ample capacity for replication, and cells that undergo a process of aging and cell death, a process called apoptosis.
All somatic cells, regardless of the system or organ to which they belong, they are haploid, so that at their core they are genetically the same. They are the mechanisms of biochemical differentiation, which make each of the somatic cells comply with a specific function and form the tissues of each organ, such as muscles, bones, neurons or blood cells red.
Almost all cells in the human body are somatic cells. The only exception are the germ cells or gametes, the sex cells, which in the woman form the ovules, and in the man the sperm. These cells only contain half of the genetic material (only 23 chromosomes).
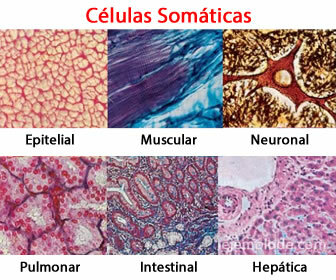
Somatic cells example:
Epithelial cells
Epithelial cells (Textus epitelialis) form a tissue in layers of united cells that finally cover the body of the living being, and in humans they make up the skin, which is the largest organ in the body, its name is epidermis.
Muscle cells
These cells are the ones that make up the muscle tissue, which in turn produce the mechanical movements of the body.
Neural Cells
These cells are the ones that make up the brain tissue, their communication is considered the fastest in the body and communicates with the rest of the body cells regardless of whether they are muscular, glandular or nervous Neural communication requires biochemical agents (hormones among others) of which serotonin stands out, the main basis of neuronal communication.
Lung cells
These cells have the specialization of filtering the blood and oxygenate it, which is produced by the alveoli, where the blood circulates. blood that is pumped by the heart and becomes oxygenated as it passes through the lungs, returning oxygenated blood to the system circulatory.
Intestinal Cells
His name is "Enterocytes”And its function is the absorption of certain substances from food, these cells are found both in the large and small intestines and in the colon.
Liver Cells
These cells, which are also known as parenchyma cells. They have the function of synthesizing the salts that enter the body, the cholesterol from food, as well as synthesizing the assimilated proteins.
Blood cells
Blood cells are of three well-known types:
- White blood cells.- These are also called “leukocytesThey are the ones that take care of the immune system and form protection against viruses, infections and injuries, they are the ones that form the pus from wounds.
- Red blood cells.- These are also called "erythrocytes”And its function is to transport the oxygen that enters the lungs to the rest of the body.
- - These are also called “thrombocytes"Are the cells that allow blood to clot and are produced in the bone marrow.
Bone cells
These cells make up the rigid structure of the body, which in our case is the human, they are divided into three and each one has a function:
- Osteoblasts.- These have what is called the complex of Golgi that helps to synthesize proteins. These cells are responsible for the formation of bones and for absorbing the necessary minerals.
- Osteoclasts.- These cells are responsible for the bones to have resorption of bone and cartilage (resorption is the reabsorption that the body has on calcium) and due to its porosity, the resorption occurs on the surface of the bone
- Osteocytes.- These cells communicate through cytoplasmic processes attracted by the canaliculi of the bone. They are osteoblasts that are housed in the back of the bone where it regenerates.
Splenic cells
It is the name given to the spleen cells, they are directly related to blood regulation, which occurs in this organ.
Pancreatic cells
These cells are one of the most important in body metabolism, as they secrete glucagon, which increases or decreases the level of glucose in the blood, adjusting it to the physical needs of the individual.
Renal Cells
Kidney cells allow the filtration of substances that are discarded by the body. These cells are polarized, which allows them to separate substances by sending waste into the urine.
Pituitary Cells
These cells promote the secretion of the hormone produced by the thyroid and prolactin.