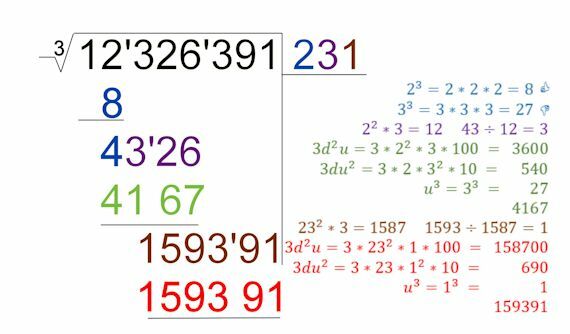
Characteristics of Plant Cells
Biology / / July 04, 2021
The cellulose they are the smallest living elements that exist, in addition to the fact that cells are only found in living beings. Therefore or the only sound acronyms of the morphological decades living being.
In addition to the fact that the following clients are formed by the sum of many cells, which produces the called organisms by cell phones, although there are also single-cell organisms (organisms unicellular).
The vegetables cells They are found in the group or division called "eukaryotic cells", since eukaryotic cells are made up of three different segments:
- Cell membrane
- Cytoplasm
- The nucleus
Then then the acronyms are cataloged in another division:
- Animal cells and
- Vegetables cells

The characteristics of plant cells are:
Cellulose.- Plant cells have a cell wall that is the outer part of the cell and is characterized by being firm or quite rigid.
Cytoplasmic membrane.- The plasma site membrane is composed of lipids.
Chloroplasts.- This is another characteristic of plant cells. These proposals allow photosynthesis, a unique and indispensable phenomenon in the plant, which synthesizes sugars and their pigment or is called chlorophyll.
Vacuole.- It is a part that if characterized by concentrating liquids and being part reaches 80 or 90% of the dimensions of a plant cell.
Mitochondria.- They are the part of cells that are common in all eukaryotic cells and allow cellular respiration.
Ribosomes.- They can be found in membranous structures.
Cytoplasm.- It is the internal fluid of the cell.
Core.- It contains the genetic information.
Parenchyma.- The plant parenchyma consists of the containment of plant tissues that accumulate or form continuously.
Meristem.- It is called meristem or meristematic tissues to the tissues that produce the growth of plants, they are capable of dividing and its shape can be defined as polyhedral, with thin walls and multiple vacuoles little; they are called totipotent cells, due to their ability to make up all plant tissues.
Structure of plant cells:
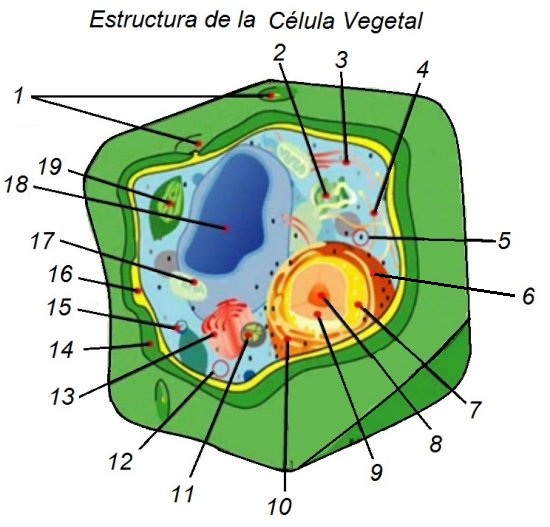
The plant cell has different parts, which will be explained below:
1.- Plasmodesmus.- This is the way in which the continuous formed units of cytoplasm are called, these can cross the cell walls establishing connections between the cells of multicellular organisms that have wall mobile. In these plasmodesmata, only about 800 Daltons are transferred.
2.- Endoplasmic reticulum.- These reticles are a complicated system formed by membranes made up of flat sacks and small tubes that are connected to each other, sharing the same internal space.
3.- Filamentous skeleton cyto.- The Cytoskeleton is an element made up of cytoplasmic proteins which can polymerize into filamentous structures, this cytoskeleton It is the one that shapes the cell and controls the movement of the cell, in addition to being subdivided into microtubules and intermediate filaments.
There are several intermediate filaments, which are classified according to the protein that composes them:
- Demining
- Nuclear sheets.
- Nestina
- Neurofilaments
- Glial fibrillar acid protein (GFAP)
- Keratins
- Vimentin
4.- Membranous Vesicle.- This vesicle has the function of participating in all cellular functions, transferring information and biochemical products.
5.- Ribosome.- Ribosomes are structures that do not have a membrane, are balloon-shaped, and are made up of proteins associated with the ribosomal RNA of the nucleolus. They can be found attached to the membranes of the reticulum or free in the cytoplasm and their function is to nexus between these structures and the messenger RNA reader assembling the amino acids that form the protein.
6.- Nuclear membrane.- The nuclear membrane is a covering or envelope also called "karyothek", its conformation is porous and it only occurs in eukaryotic cells.
7.- Nucleolus.- This is a part considered supra macromolecular, as it does not have a membrane that limits it and its function is the duplication or transcription of ribosomal RNA, for this it uses the polymeraza1 and the subsequent formation of ribosomes by the pre-components, including in their functions the regulation of the cell cycle, aging and the functions of the theomerase. Chromatin is the element that contains the whole DNA of the plant, here are the stomata and the chromatin of the plant.
8.- Core.- The cell nucleus has the characteristic of being formed by two membranes and within these it houses the genetic material DNA and is typical of eukaryotic cells.
9.- Rough endoplasmic reticulum.- This is intended to transport and synthesize proteins, it is typical of eukaryotic cells.
10.- Tonoplast.- It is a type of membrane that surrounds the vacuole, directly delimits the cell, its relationship is directed to the pressure of the cell sap.
11.- Cytosol or cytoplasm.- This forms about 50% of the cell volume, this is the soluble section and is composed of organelles or proteins, ions, glucose, nucleic acids, metabolites and nucleotides.
12.- Tonoplast.- This is a membrane that sets a boundary to the central vacuole in plant cells. It has a partial permeability that selects certain ions to the vacuole; This phenomenon allows you to partially concentrate water with little energy consumption.
13.- Golgi apparatus.- This is the cellular organ responsible for the transmission of chemical information, it is found in all eukaryotic cells. Its function is to expel proteins and lipids out of the cell, which it transforms to be able to dispose of them and the dictionsoma It is a set made up of between 6 and 30 small cisterns that make up the so-called Golgi apparatus, and they are sacks stacked one on top of the other forming a set that produces some proteins.
14.- Cell wall.- This has the function of protecting and is found in fungi and plants, its structure is usually sheet, it is found in The exterior of the plasma membrane and in plants is composed of cellulose, which is a polymer composed of carbohydrates. Starch is a compound of the plant, this is the source or reserve of plant food, and its composition is made of "amylose" and its properties are 3000 glucose units. approximately, which forms 30 or 35% of the starch and the second compound is amylo-pectin, which completes the rest of the starch and is composed of a range of 2000 to 200,000 units of glucose.
15.- Peroxisome.- Perixisomes are organelles typical of eukaryotic cells that contain "oxidases and catalates", which are cellular detoxifying enzymes.
16.- Plasmatic membrane.- This is the surface layer of cells, it delimits the intracellular zone with the extracellular one, it is made up of proteins, glycolipids and Phospholipids, having a sheet or cover form, have the quality of allowing the entry and exit of some substances that are thus required by the cell.
17.- Mitochondria.- These are organelles that provide energy by metabolizing reserved energy, as well as they are an important part of cellular respiration and are the basis of ATP sitetization by metabolic fuels.
18.- Vacuole.- This is an almost exclusive characteristic of plant cells, it is about laminated sacks that go joining others when the plant grows and inside the sac there is liquid (water) with nutrients, generally sugars. In general, the plant has a single vacuole, which is sometimes made up of several fused vacuoles.
19.- Chloroplast.- This is an element that in the cellular organelles of plant eukaryotes produces the so-called photosynthesis, they are formed by thylakoids which are a membrane structure that is made up of flattened sacs and allows photosynthesis of plants.