Characteristics Of The Planets
Astronomy / / July 04, 2021
Planets are opaque stellar bodies orbiting a star.
The word planet means wanderer or walker and this name was given to the bodies that are observed moving in the night sky at a different speed than others. First they were called planets to those that orbit around the Sun, and later any object in the outer space that fulfills a series of characteristics was called thus.
The main characteristics of the planets are:
One of the main characteristics of the planets, is that they do not have their own light, that is, they are opaque bodies, but it is possible to see them when turning around a star, as they reflect its light, allowing them to be observed in the sky night.
Another of the characteristics of the planets that a celestial body must meet to be considered as such, is its spherical shape, which is due to the fact that These have a sufficient amount of mass to achieve a force of gravity, which gives them their shape spherical.
The planets' force of gravity absorbs small bodies that may be in their orbital path, which is why they are said to have a clean orbit.
When the planets are revolving around the Sun they are called solar planets; when a planet is located revolving around another star different from the Sun they are known as extrasolar planets.
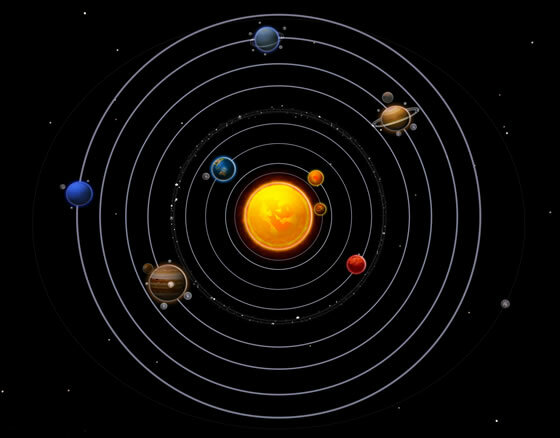
According to the characteristics of each planet, they are classified as:
- Terrestrial: Also known as telluric planets, they are of great density and small in size. Its soil is rocky and firm. The planet Earth, Venus and Mars belong to this type.
- Gaseous: This type of planet is characterized by its large size and low density that is due to the fact that they are formed mainly gases, such as the planet Jupiter, hence they are also known as planets Jovians. Its atmosphere is made up of hydrogen and helium as main components; examples of these are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
- Dwarf planets: This classification is created recently to call celestial bodies that are not sufficiently large to be considered a planet, but not small enough to be considered a planet asteroid. Pluto is an example of this.
As the planets do not emit their own light and in general, no type of radiation that can be detected by any instrument, the existence of these outside the Solar system occurs by indirect means, either by the light that reflects from the star it orbits, or by the deformation of space-time that it generates around of the.
