Composite Materials Example
Chemistry / / July 04, 2021
The Composite materials are those who are constituted by two or more pure substances, unlike Simple Materials, which only contain a pure substance.
Characteristics of a Composite Material
A Composite Material it is usually a homogeneous mixture, that is to say that its components are indistinguishable, so only one phase can be seen with the naked eye.
The components of a Composite Material do not chemically react with each other. It is only limited to its character as a Physical Mix.
It is very difficult to separate Composite Material in its main components, since it is practically a new substance.
Being a mixture, it is understood that it was necessary to incorporate several pure substances, each with its own characteristics. Therefore, it follows that the Composite Material is generated to have in a single Material the properties of all individual substances.
Its properties, better than those of the initial substances alone, are characterized by fulfilling a specific function in human activities. It can be in domestic tasks, commercial activities or in industrial requirements.
Obtaining Composite Materials
Composite materials are obtained by mixing the substances that will compose it. This mix can be achieved in several ways:
Agitation: There are times when there are components in various states of aggregation, such as liquid and solid. In the mixing container, the main substances will be emptied, and thanks to the help of a stirrer, they will be involved evenly, without bubbles or clumps. The consistency will remain the same at each point of the Composite Material. An example of a Composite Material obtained by stirring is cake or pastry dough.
Heating: When the components are metals or solids, and they have a high melting point, they are taken to a melt, which is an extreme heating that takes them to the liquid state, so that their internal structures remain well alternated by the time they solidify again. An example of a composite material obtained by the heating method are alloys, which are the mixture of two or more metals, to obtain metals with more mechanical resistance.
Composite Materials do not normally originate in nature, but must be generated by one of the procedures between stirring and heating, also using separation processes such as grinding, grinding and sieving.
Cake dough: This composite material is the raw material for the baking industry. It is made up of Wheat Flour, Water, Salt, Sugar, Sodium Bicarbonate and Yeasts. Each of these components cannot form a loaf or a cake on its own. The mass is the result of its mixing by stirring. In the end you will have a fermented, crisp and good-tasting product.

Cement: The main element to ensure the construction, Cement, is a powdery mixture of various chemical compounds, such as Carbonates, Silicates, Sulfates and Hydroxides. It is a fine-grained gray powder, in which the components are not distinguished. This composite material, when mixed with water, generates Concrete, a greyish and dark paste that will be interposed between the partitions or blocks, holding them like glue. The property of Concrete is that it will dry, leaving a strong structure. The chemical compounds that form it still do not react chemically. The alternation of its particles in the mixture of dust and water is enough to generate the properties of Concrete.

Amalgams: Amalgams are mixtures of the liquid metal Mercury (Hg) and some other element. They were originally used in dental offices to cover damaged teeth. When a tooth was partially destroyed, the usual bite tended to degrade it more and more, so the function of the amalgam was to "rebuild" the tooth, adapting the shape to how it was complete. The metal Mercury by itself represents too great a risk to human health, because it affects the Central Nervous System. However, when mixed with other metals in amalgams, its danger drops to a level that is not harmful to humans.
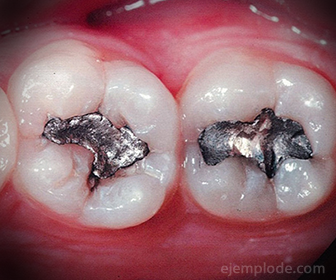
Steel: Steel is in the category of alloys. Alloys are mixtures of metals in which we seek to obtain a Composite Material with better characteristics, such as mechanical resistance, hardness, gloss, electrical conductivity or thermal conductivity, for example. Steel is then a Composite Material formed mainly with Iron and another metal, which can be Tin. Sometimes during the melting of the metals, Carbon is added, to improve the hardness of the Steel, and make it not brittle. The function of Carbon in this process is to alternate its atoms in the structure of the main alloy.

Bronze: Bronze is, like Steel, an Alloy. It is made up mainly of Copper and Tin. It is a Composite Material mainly used for Olympic medals and interior decoration. It has been used to manufacture headboards, complete bedrooms, mirror frames, structures for dining tables. Copper is not used directly due to its cost and its high electrical conductivity. In addition, Bronze is a more chemically stable resulting material and retains its shine, unlike Copper, which, when oxidized, takes on a bluish-green color.

Emulsions: Emulsions are also composite materials. Among them are Mayonnaise, Hair Styling Gel and Body Cream, for example. Its main components are naturally incompatible in a mixture, as there are oils and there is water. The main mixture would be divided into two or more phases by density separation. An emulsifier is added, which is a substance that is responsible for homogenizing the mixture, to convert it into a Composite Material of a single phase. Thus, the nutritional, capillary fixation and body moisturizing purposes will be achieved, if applicable.

Examples of Simple Materials
To have a point of comparison, several examples of Simple Materials are listed below, which have the function of serving in the elaboration of Composite Materials.
Sodium Chloride or NaCl Table Salt, the quintessential flavor enhancer for domestic and industrial foods.
"Saccaromyces Cerevisiae", or Yeast for beer and bakery
Sucrose or Cane sugar C12H22OR11, traditional sweetener for all food purposes.
Glycerol or Glycerin C3H8OR3, moisturizing ingredient in body creams.
Silicon Dioxide SiO2, main component of sand.
Potassium Nitrate KNO3, the explosive ingredient in gunpowder.
Metallic iron Fe, the indispensable component of Alloys like Steel.
Zinc metallic Zn, which is the protagonist of the galvanizing process, to generate materials coated by it.
Calcium Sulfate Ca (SO4)2, mixed with water, forms plaster, a composite material that serves to cover porosities or cracks in the walls, thanks to the fact that it has a very fine grain size and the paste is very soft.
Sodium Fluoride NaF, is the active ingredient and whitening in toothpaste.
