Example of organic reactions
Chemistry / / July 04, 2021
1. Substitution, addition and elimination reactions.
Substitution reactions. They consist of substituting a hydrogen for a different radical. The families that present this type of reaction are: alkanes, cycloalkanes and benzene derivatives.
EXAMPLE OF SUBSTITUTE REACTIONS:
CH 4 + Cl 2⇒ CH 3 - Cl + HCI
Addition Reactions: As the name implies, a certain reagent is added to the molecule of a substance. The families that present this type of reaction are alkenes and alkynes.
EXAMPLE OF ADDITION REACTIONS:
CH 2 = CH 2 + HBr ⇒CH 3 - CH 2 - Br
Elimination reactions: As its name implies, a part of the molecular structure is removed by means of a reagent.
EXAMPLE OF ELIMINATION REACTIONS:
CI-CH 2 - CH 2 - Cl + 2Na ⇒CH 2 = CH 2+ 2NaCI
2. Condensation and hydrolysis reactions.
Condensation reactions: Two molecules join together to form one.
EXAMPLE OF CONDESSATION REACTIONS: Citrate formation in the Krebs cycle or of Citric acid from Acetyl Coenzyme A Y Oxaloacetate.
Hydrolysis reactions: A molecule of Water. With the help of an enzyme or a catalyst, it breaks a bond and becomes part of the structure of compounds.
EXAMPLE OF HYDROLYSIS REACTIONS:
Breakage of the ester bond in the Triacylglycerides to give as products fatty acids and Glycerol, using an enzyme lipase what is the type hydrolase.
3. Addition and condensation polymerization reactions.
Addition polymers or chain polymerization reaction. In this type of reaction, the monomer molecule always contains at least one double bond. Example: polyethylene. An inhibitor is used when you want to end a chain reaction, as it prevents the formation of more free radicals (-CH 2 - CH 2 -). Some amines, phenols, and quinones act as inhibitors.
Initiation stage: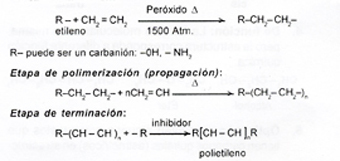
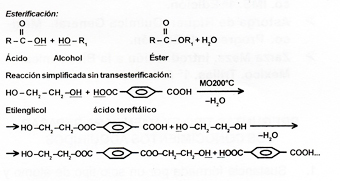
Condensation polymers: They are reactions in which two or more different molecules (monomers) are joined and a molecule of water or alcohol is eliminated. Also called step polymerization reaction. Example: Esterification.