Heterocyclic Compounds Example
Chemistry / / July 04, 2021
There are cyclic chemical compounds that are made up of only Carbon atoms, with their valences supplemented by Hydrogen atoms. Such compounds are called homocyclic. A heterocyclic compound It is an organic substance that contains a ring formed by more than one type of atoms; Besides Carbon, the most common are Nitrogen, Oxygen and Sulfur. These different atoms are called heteroatoms.
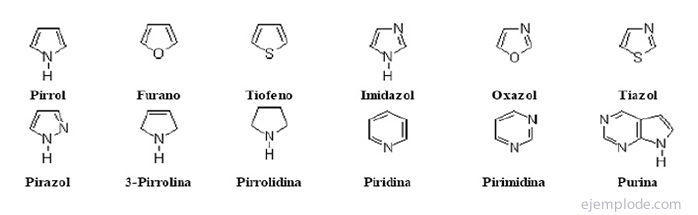
The above compounds are called Trivial names, that is, Trade names that do not provide structural information about the molecule, but that have been accepted and recognized by the IUPAC.
Classification of heterocyclic compounds
Heterocyclic compounds are classified according to two main criteria: the Type of Links that contains (if they are single or double), and in Number of rings that has.
For him Type of Links they contain, are classified into Alicyclic Compounds, when its bonds are single, or double but the geometry has 5 atoms or less; Y Aromatic Compounds, when they have a ring of Benzene in its structure, or what is the basis on which the heteroatom exists.
For him Number of rings you have, can be classified as Monocyclic, Bicyclic, Tricyclic, and a successive numeric prefix is added where appropriate.
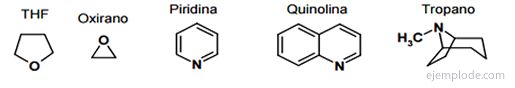
Heterocyclic compounds of three atoms
There are heterocyclic rings of three atoms that are very reactive due to their ease of opening by nucleophiles, called Epoxides and Aziridines. They are valuable starting materials in organic synthesis.
The Epoxides, also called Oxyrans, are cyclic ethers that consist of the union of an oxygen atom to two consecutive carbon that in turn form part of a chain of covalent bonds. It is a triangular structure whose base is Carbon and the vertex is Oxygen. They are colorless liquids, soluble in Alcohols, Ethers and Benzene. The simplest term is Ethylene oxide, also called Epoxyethane or Oxirano. Its synthesis is more frequent by the breaking of a double bond between the Carbon atoms with acids that contain several Oxygen atoms. They are named indicating the positions in which the oxygen atom is attached, followed by the prefix "Epoxy-" and the name of the hydrocarbon that supports it.
Present in polymers, they are used as plastic for structures, coatings and adhesives. In addition, they have an important participation in the manufacture of abrasives, friction materials, in the textile industry, in cast iron, filters and lacquers. Also for mineral wool, impregnations, wood materials, foams, molding powders. In the food industry, epoxies are used as chemical sterilants in low moisture foods and aseptic packaging materials.
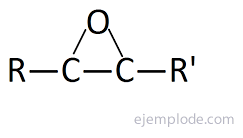
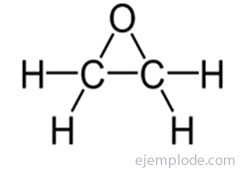
The AziridinesAs well as Epoxides, they have a triangular structure, only that the heteroatom is Nitrogen. They are colorless liquids, soluble in water, poisonous and with an ammonia odor. They have a special physical property that is attributed to the geometry of the ring; the nitrogen atom has a significantly higher barrier to pyramidal inversion than other monocyclic and acyclic amines. A useful procedure for the synthesis of aziridine is the pyrolysis or photolysis of 1,2,3-triazolines. These compounds are readily prepared by reacting azides with alkenes in a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reaction.
By evaporation, Aziridine can reach harmful concentrations in air at 20 ° C. Reacts with oxidizing agents and is prone to combustion, generating Nitrogen oxides.

Heterocyclic compounds of five atoms
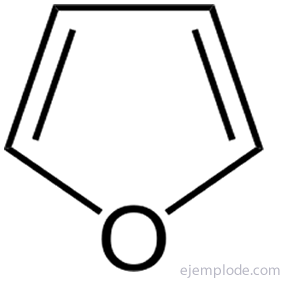
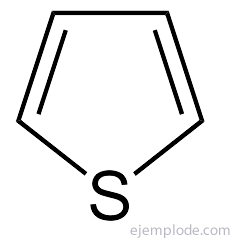
The simplest of the five-atom heterocyclic compounds are: Pyrrole, with Nitrogen heteroatom, Furan, Heteroatom Oxygen and Thiophene, Sulfur heteroatom.
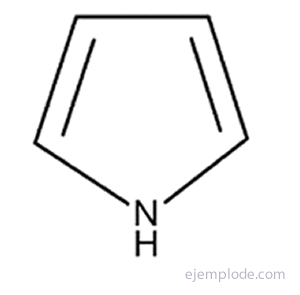
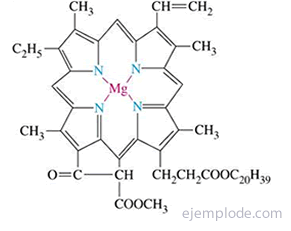
The Pyrrole ring is the fundamental unit of the porphyrin system found, for example, in Chlorophyll and Hemoglobin.
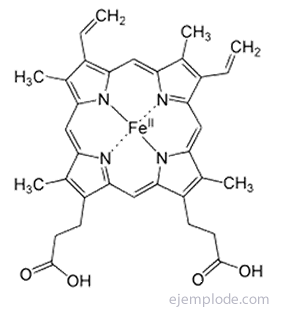
Pyrrole is found in small amounts in coal tar, as is Thiophene. By fractionally distilling tar, thiophene (boiling point 84 ° C) is collected together with Benzene (boiling point 80 ° C).
The easiest way to obtain Furan is by decarbonylation (Carbon Monoxide Removal) of Furfural (furfuraldehyde) which, in turn, is obtained by treating oat or rice husks, or corn cobs, with acid boiling hydrochloric.
Heterocyclic compounds of six atoms
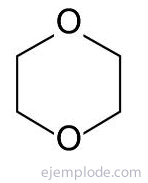
Of the saturated terms, one of the most important is 1,4 Dioxane or Dioxane, which is a liquid colorless, with a characteristic odor, whose vapor is denser than air and can spread along the I usually. May form explosive peroxides in contact with air. Reacts with oxidants and strong acids. Reacts violently with some catalysts.
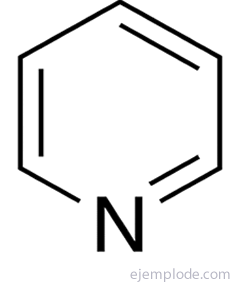
Of the unsaturated heterocyclics, one of the most important terms is Pyridine, which consists of a benzene ring structure with a Nitrogen heteroatom. It is the precursor configuration for many vital molecules such as deoxyribonucleic acid components.
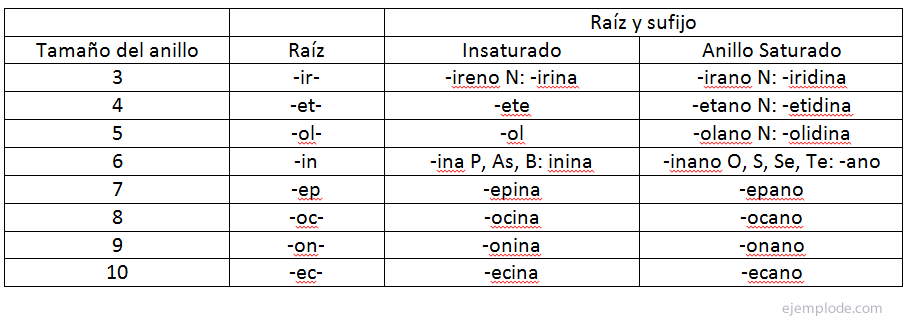
Systematic Nomenclature of Heterocyclic Compounds
For heterocyclic compounds of a Ring (Monocyclic), the appropriate nomenclature is derived by combining a prefix and suffix appropriate to a certain root, according to the following rules:
The prefix denotes the nature of the heteroatom, the Root explains the size of the ring, and the Suffix determines the degree of unsaturation. The order to follow in the Nomenclature is Prefix-Root-Suffix.
The nature of the heteroatom is denoted by prefixes like oxo for Oxygen, uncle for Sulfur or aza for Nitrogen.
The heteroatom multiplicity is designated by an additional prefix, such as di, tri, tetra, etc.
When there are two or more different heteroatoms, they are named with the following priority: O> S> N; for example Oxazo for Oxygen and Nitrogen, Tiazo for Sulfur and Nitrogen, Oxatio for Oxygen and Sulfur.
The ring size it is denoted by the proper stem.
The degree of unsaturations is specified by the suffix. It should be noted that the suffix is slightly modified when there is no nitrogen in the heterocyclic ring.
Ring numbering begins with the highest priority heteroatom and continues around the ring, assigning the lowest possible numbers to the other heteroatoms or substituents.
When a system that has the maximum number of double bonds still contains a saturated atom in the ring, it is indicated by a number indicating its position and the letter H- capital italic as a prefix.
