Characteristics Of Halogens
Chemistry / / July 04, 2021
Halogens are the chemical elements that are located in group VIIA or group 17 of the periodic table. It is made up of the elements fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine and astate.
The name halogen comes from the Greek and means "producer of salts", since these elements form salts with sodium similar to common salt.
Common characteristics of halogens:
They are monovalent elements, that is, they only have one valence number. In halogens the valence is -1.
They have an affinity for hydrogen, forming the so-called hydracids.
They have little affinity for oxygen, so they do not form oxides but at very high temperatures.
They combine with metals to form halogen salts.
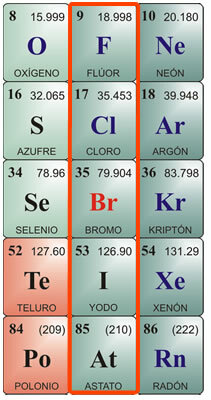
Individual characteristics of halogens:
Fluorine Characteristics:
Chemical symbol F. Atomic number 9, atomic weight 19. Fluorine in its pure state is a yellow gas, with a melting point of -223 ° C and a boiling point of -187 ° C. It does not exist free in nature, so it must be isolated. It was first isolated in 1886. Its physical characteristics are: Greenish-yellow gas, Very corrosive and irritating, with a pungent odor, poisonous to humans and animals. It is difficult to liquefy. Chemical characteristics: It combines with hydrogen, even at very low temperatures with an exothermic reaction. It combines with metals, forming salts. It decomposes hydrochloric acid, producing chlorine, and decomposes water, releasing oxygen. Due to its affinity for hydrogen, it takes it from organic substances, carbonizing them. One of its main compounds is hydrofluoric acid, which can only be stored in platinum or wax jars, as it attacks the silica in glass. It is very volatile and very corrosive. When combined with metals, it produces fluorides.
Chlorine Characteristics:
Chemical symbol Cl. Atomic number 17, atomic weight 35.5. Melting point - 102 ° C, boiling point -37 ° C. Chlorine was discovered in 1774 and isolated in 1811. Physical properties: It is a greenish-yellow gas, which does not exist free in nature, since it is generally found combined in salts. It has a suffocating and poisonous odor. Chemical properties: Chlorine is very akin to hydrogen, combining in an exothermic reaction to produce hydrochloric acid. Hydrochloric acid, also called muriatic acid or fuming salt, was known since ancient Rome. It was found in a gaseous state in volcanoes, and dissolved in the water of some rivers near the volcanoes. It is very corrosive to the skin and poisonous if ingested. It is produced by the stomach for digestion. Other important chlorine compounds are hypochlorites, especially sodium hypochlorite, which, when dissolved in water, is used as a water bleach, disinfectant, and sterilant. Neutralizes acids.
Bromine characteristics:
Chemical symbol Br. Atomic number 35, atomic weight 79.9. Melting point -7.3 ° C, boiling point 58.8 ° C. It is not found free in nature, but combined with metals to form bromides. It is isolated by electrolysis. Physical properties: It is a dark red liquid with an irritating odor; at room temperature gives off an irritating dense orange-red vapor, causing coughing and tearing; It is poisonous. It dissolves in ether or chloroform and hardly dissolves in water. Chemical properties: Bromine attacks organic matter; in living beings it corrodes the skin and causes ulcers that are difficult to heal. Its main use is combined with metals forming bromides, used for industrial uses, such as silver bromide, formerly used in photography. They are also used in low concentrations as an antiseptic. Combined with hydrogen, it results in hydrobromic acid, a colorless gas with a pungent odor and taste, used mainly to attack metals and obtain bromides.
Features of the Iodine:
Chemical symbol I. Atomic number 53, atomic weight 126.9. Melting point 113 ° C; boiling point 184 ° C. It does not exist free in nature. It is found as iodides in seaweed beds and as part of the minerals in some foods, such as watercress, cod oil, and shellfish. Physical properties: Iodine is a solid, crystalline body, blackish gray in color, with metallic luster, with a strong and unpleasant odor. It is poorly soluble in water and very soluble in alcohol. Chemical properties: It combines with metals forming iodides; also with metalloids, such as sulfur and phosphorus. It has a higher affinity for oxygen than the other halogens. When combined with ammonia it produces nitrogen iodide, which is an explosive gas. Combined with hydrogen, it produces hydroiodic acid, a colorless gas with a pungent odor and taste, which smokes in the presence of air. It dissolves in water and decomposes under the action of light and heat. If the acid molecule contains oxygen, then ioic acid is produced, which is a crystalline solid with oxidizing characteristics. Iodine is used in alcoholic solution as a disinfectant and antiseptic.
Features of the Astatus:
At symbol. Atomic number 85, atomic weight 210. It does not exist free in nature. Melting point 254 ° C; boiling point 962 ° C. Astatine was first synthesized in the 1940s, as it is an element that is released from the breakdown of bismuth atoms by alpha rays. It is a radioactive element with a very short life; the isotope that lasts the longest is At210, with a maximum life of about 8 hours. Its chemical properties are considered to be very similar to those of iodine; physically it could have an appearance and properties more similar to those of metals. Despite being a radioactive element, it does not pose a health hazard, as it is not normally found in nature. It has only a few applications in the laboratory, for the labeling of atoms in the study of subatomic matter.
