Example of Chemical Phenomena
Chemistry / / July 04, 2021
Chemistry studies the component elements of matter, the compounds they form and their possible combinations, the products resulting from these combinations and their structure, and the phenomena that produce, accelerate or retard these modifications. A Chemical phenomenon is one in which two or more substances undergo a change that alters their internal structure, giving rise to one, two or more substances, different from the original matter.
Unlike physical phenomena, in which some properties of objects are altered, but they are always the same substance or compound, in physical phenomena the structure of substances is altered, leaving as a result, other substances different from those originals. That is to say that all chemical phenomena are chemical reactions, which result in one or more substances that are molecularly different from the original substance or substances.
Types of chemical phenomena:
Chemical phenomena can be classified in relation to the result as follows:
Synthesis
Two or more compounds join together to form a more complex compound.
Decomposition
A complex compound breaks down to form simpler molecules.
Displacement
One of the elements or a radical of the reacting molecules becomes part of the other molecule with which it reacts.
Double scroll
The reacting molecules exchange an element or a radical, giving rise to two different molecules to which they reacted.
Now, regarding reactions as chemical phenomena, we can mention the following:
Oxidation
Oxidation is a reaction in which oxygen combines with another element, giving an oxide, in the case of metals, and an oxy-acid if it combines with non-metallic elements. The reaction is slow and the temperature of the material does not increase.

Combustion
Combustion is a form of rapid oxidation, in which light and heat are also given off, that is, it is an exogenous reaction.
Alkalization
It is when a metal combines with a hydroxyl radical (radical with the -OH form).
Acidification
It is when a non-metallic element is combined with hydrogen
Neutralization
It is the combination of a hydroxide with an acid, resulting in the formation of water and a salt.
Reduction
It is the elimination of oxygen from an oxide, to obtain the pure metal, by the reaction with hydrogen from an acid.
Ionization
When dissolving a salt in water, the elements that compose it are separated into atoms with electrical charges, which can be positive (cation) or negative (anion). These types of solutions are called electrolytes.
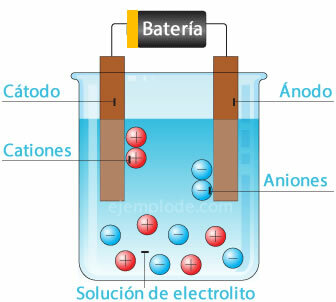
Electrolysis
When an electric current is passed through an electrolyte, the electricity causes atoms to break off from the water. the hydrogen ion, with a positive charge, going to the negative pole (cathode), and the oxygen, with a negative charge, going to the pole positive (anode). When electrolysis is applied in an acid, one of the effects is to displace the metallic element to the anode.
Catalysis
Two substances that under general conditions do not react, or do so very slowly, can react in very quickly in the presence of a third substance, which will not undergo changes before or during the reaction. This type of substance is called catalysts.
Fermentation
It is the obtaining of a chemical change, especially in organic compounds, by the action of bacteria.
Example of chemical phenomena:
1. An unpainted grill will have contact with oxygen in the air and water, and will begin to show rust (oxidation)
2. Bringing a wood close to the fire will cause it to burn, causing some of the carbon molecules that make it up to mix rapidly with oxygen, releasing carbon dioxide, leaving burnt wood and soot as a residue (combustion)
3. The decomposition of food is due to the digestive action of bacteria, which alter the chemical structure of the components. (Fermentation).
4. The car battery produces electricity by the reaction between the electrolyte and the metallic cells with which it is formed, causing the release of ions that produce electricity. To charge it, the current flow performs an electrolytic action that returns the ions to the plates.
5. The gases produced by the automobile engine, it is stable and hardly decomposes after it has left the engine and reaches room temperature. The catalytic converter contains a platinum foam, which, when heated to approximately 500 ° C, allow gases to break down into simpler compounds, without the platinum being modifications.
6. By dissolving salt in water, it splits into sodium and chlorine ions.
7. The fizz that occurs when you mix lemon juice with baking soda is a neutralization reaction.
8. When we bleed, the blood takes on a darker color, due to the oxidation of iron found in red blood cells. This is also why venous blood is darker, and arterial blood brighter.
9. The chrome plating of automobile parts uses electrolysis to deposit the chrome on the metal part that is being chromed.
10. In digestion as a chemical phenomenon, the action of hydrochloric acid on food is to break down the complex molecules that form them, into smaller molecules that can be more easily absorbed into the intestine.
