Peptide Bond Example
Chemistry / / July 04, 2021
The Peptide Bond is the one in which two amino acid molecules are joined by condensation.
To better understand peptide bonds, Amino Acids must first be defined:
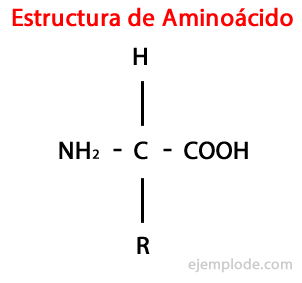
The Amino acids are organic molecules short containing at least an amino group (-NH2), alkaline in nature, and a carboxyl group (-COOH), acidic in character.
Although living beings synthesize, for different purposes, very diverse types of amino acids, the most important are those that are part of proteins, all of which belong to the class of the α-amino acids.
The α-amino acids are characterized by having the acid and amino groups attached to the same carbon atom, called α Carbon. Furthermore, this α-carbon binds, as a third substituent, a hydrogen atom and, as a fourth substituent, an additional group of diverse size and characteristics, which differentiates each amino acid from others.
The fourth substituent is called Side Chain of the Amino Acid and is often represented in simplified form by the letter R.
As the four substituents of the α-carbon are different, and adopt a tetrahedral arrangement around it, the α-amino acids present
optical isomerism, which is when a molecule has a alternate form that looks like a mirror image his, which in the end is not an equal molecule. These two isomeric forms of the molecule are assigned the letters D or L, depending on how the substituents are arranged in space. All the amino acids that are in proteins are L.Amino acids are classified according to their chemical character in Polar and Apolar. The Polars in turn are divided into Neutral and Charged (which can be acidic or basic). The Non-polar can be Aliphatic or Aromatic.
Peptides and the Peptide Bond
Peptides are the product of the covalent union of amino acids through Amide Bonds, forming by condensation of the Carboxyl end of one and the amino end of the other, releasing a water molecule in the reaction. This union is called Peptide Bond.
The mechanism of this reaction is presented below, in which the Amino and Carboxyl Groups, and the condensation of the Amino Acid molecules occurs to form the Peptide.
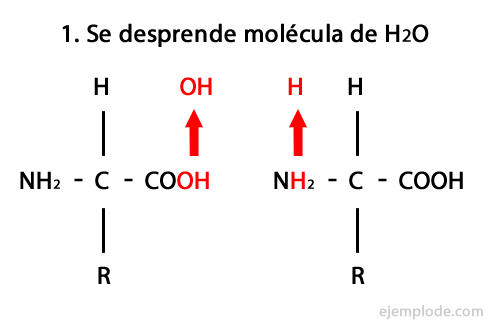
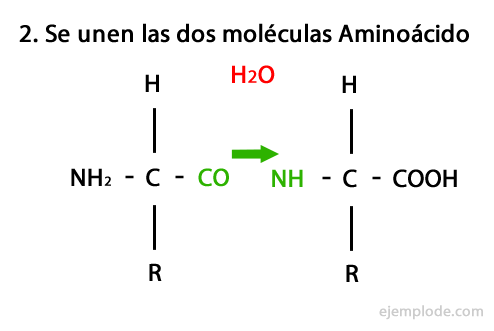

Peptides, like amino acids and proteins, have an amino group and a carboxyl group at their ends without reacting.
To specify the formula of a simple peptide, and even a protein, it is enough to list the amino acids that compose it, starting with the one with a free Amino group, and ending with the one with its free Carboxyl group.
Some peptides found in the body are the Vasopressin, which raises blood pressure and increases water reabsorption in the kidney; the Enkephalin, which reduces the sensation of pain; and the Oxytocin, which causes the uterus to contract.
Peptide Bond Characteristics
The condensation of the Amino group of one amino acid with the Carboxyl of another, takes place in aqueous solvent, so that it is not spontaneous, and therefore protein synthesis requires a supply of energy.
The Peptide Bond, as in any amide bond, presents resonance between two extreme forms: the neutral form, with a single bond joining the carbonyl carbon of the first amino acid and the amino nitrogen of the second (C-N), and the form with separation of charges in which the two atoms are linked by a double bond (C = N). In reality, the peptide bond does not adopt either of the two extreme situations, but is a resonant hybrid of both.
There is the call Peptide Plane, consisting of all the atoms involved in the Peptide Bond, which join the two initial amino acids. On the one hand, the atoms of Nitrogen and Hydrogen, with their respective Carbon α in the first amino acid. On the other, the Carbon α of the other amino acid, with the Oxygen and Carbon of the Carbonyl group.
Differences between Peptides and Proteins
The peptides have a low number of amino acids, which ranges from two to a few dozen of them, and their conformation in solution becomes flexible.
The small proteins, structurally close to large peptides, have a defined conformation and much less flexible.
There are proteins that, like peptides, have a disordered and flexible conformation, but that order when they interact with other macromolecules in the cell.
20 examples of Amino Acids that participate in Peptide Bonding
- Wisteria
- To the girl
- Valine
- Leucine
- Isoleucine
- Proline
- Methionine
- Phenylalanine
- Tyrosine
- Tryptophan
- Serine
- Threonine
- Cysteine
- Asparagine
- Glutamine
- Aspartic acid
- Glutamic acid
- Lysine
- Arginine
- Histidine


