Example of Profit On Sales
Accounting / / July 04, 2021
Profit on sales. Once the value of net sales and the cost of sales have been determined, profit on sales is determined by subtracting the value of cost of sales from net sales.
Example:
Considering the net sales and the cost of what was sold in the previous cases, the profit on sales would be:

The profit from sales is also called gross profit.
Observation. When the cost of goods sold is greater than the value of net sales, the result will be the loss on sales or gross loss.
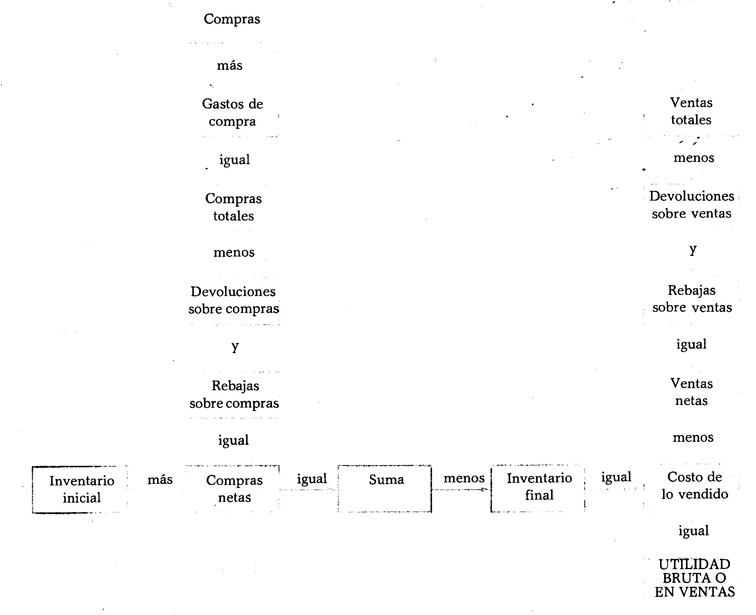
Use of columns. As in the Balance Sheet, the Profit and Loss Statement uses four columns to record the amounts. The following indicates in which column the value of each of the elements that makes up said status is noted.
First column. In this column you must enter the values of purchases, purchase expenses, returns on purchases and discounts on purchases.
Second column. In this column, the values of returns on sales, discounts on sales and total purchases must be entered.
Third column. In this column you must enter the values of total sales, beginning inventory, net purchases and ending inventory.
Fourth column. In this column, the values of net sales, cost of goods sold, and profit or loss on sales should be entered.
Changes in placement.
1. When there are no returns or rebates on sales, the value of the total sales goes directly to the fourth column, as if they were net sales.
2. When there are no purchase expenses, the value of the purchases goes directly to the second column, as if it were total purchases.
3. When there are no purchase expenses or returns and discounts on purchases, the value of the purchases goes directly to the third column, as if they were net purchases.
4. When there are only returns on sales or rebates on sales, their value goes to the third column.
5. When there are only returns on purchases or discounts on purchases, their value goes to the second column.
How to obtain the profit in sales