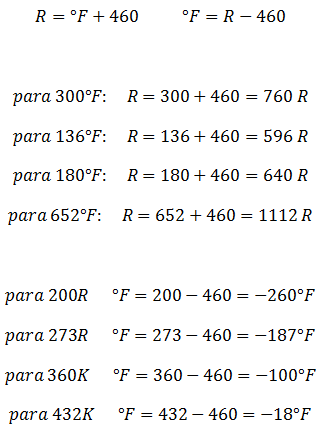Temperature Conversion Example
Physics / / July 04, 2021
Temperature is the physical quantity that indicates the kinetic energy (energy of movement) average that the constituent particles of a substance possess. Temperature is susceptible to being increased or decreased, thanks to the phenomenon of Heat, which is the natural transfer of this kinetic energy from a hotter substance to another that is less hot measure.
Temperatures or degrees of heat are measured by devices called Thermometers. The most widely used Thermometer is the Mercury Thermometer, which is a liquid metal whose thermal expansion is remarkable. The thermometer consists, from bottom to top, of a small deposit with mercury, followed by an internal capillary through which the small expanse of Mercury will rise. In a graduated, transparent external structure, the expansion of the metal will be appreciated, and the temperature of the environment or the substance under measurement will be appreciated.
The scale of a thermometer has two fixed points, which are the Freezing point and the Boiling point of the water. at barometric pressure of 760 mm.
Celsius and Fahrenheit scales
In the centigrade or Celsius thermometer, the scale established for the International System of Units, the Freezing Point of Water corresponds to Zero, and the Boiling Point to 100. The space between the fixed points is divided into 100 equal parts called Degrees.
There is another scale that is Fahrenheit, in which the freezing point of water marks 32 degrees, and the boiling point 212 degrees. The space in between is divided into 180 equal parts.
For the conversion from degrees Celsius or centigrade to degrees Fahrenheit, the procedure is as follows:
The degrees Celsius are multiplied by 1.8, and then 32 more degrees are added. Each step will be explained in a paragraph:
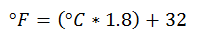
The degrees Celsius are multiplied by 1.8, because the space included in one degree centigrade equals the travel of 1.8 degrees Fahrenheit. This will be noticeable at first glance if both scales are compared. For a path from the freezing point of water to the boiling point of water, the Celsius scale has 100 steps; and the Fahrenheit scale has 180 steps.
32 degrees are added to the conversion, because if we compare the scales again, the fixed freezing point is is at 0 degrees in the Celsius, and the same fixed freezing point is at 32 degrees in the Fahrenheit. To find out Fahrenheit degrees, you need to consider the first 32 degrees below.
If we have degrees Fahrenheit, what is done is the reverse procedure: Subtract 32 degrees from the current scale, and then adjust to Centigrade, dividing by 1.8. So we will have the result in degrees Celsius.
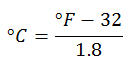
Absolute Kelvin and Rankine Scales
If the temperature of a substance were reduced to minus 273 ° Celsius, its molecules would be completely at rest, and it would have no heat. It would be absolutely cold. It is at this point where Absolute Zero is established, which is precisely that temperature at which matter cannot be colder.
An Absolute Scale, called the Kelvin Scale, was established to encompass all possible temperatures in the known universe. It is associated with the Celsius or centigrade Scale in its division into degrees, and its beginning is at absolute zero, which are: 0 K.
There is also an Absolute Scale that is associated with the division into degrees of the Fahrenheit scale, and is called the Rankine Scale. It is also located from 0 R, which corresponds to -460 ° F.
With an initial focus on the Centigrade Scales, the conversion between Celsius and Kelvin will be explained.
Taking a value in degrees Celsius, what you have to do is add the 273 involved in the absolute scale. This will finally have the value in degrees Kelvin. As an example, at the freezing point of water, at 0 ° Celsius, there are already 273 Kelvin.
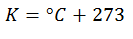
When you have a value in Kelvin, only the 273 degrees leading to absolute zero are subtracted, to be on the Celsius scale again.
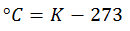
When having a data in degrees Fahrenheit, what you have to do to convert it to absolute degrees Rankine is to add 460 degrees.
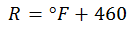
To calculate Fahrenheit degrees from Rankine absolutes, just subtract 460 degrees.
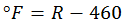
Examples of Temperature Conversion
Conversion from Celsius to Fahrenheit:
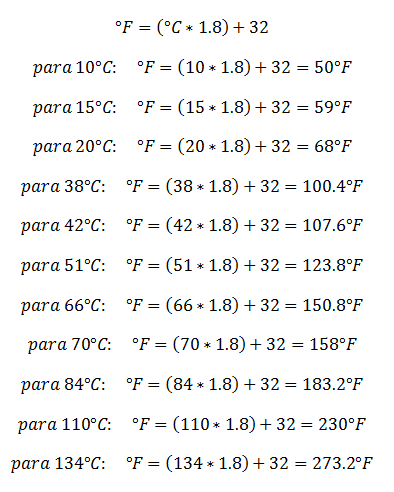
Conversion from Fahrenheit to Celsius:
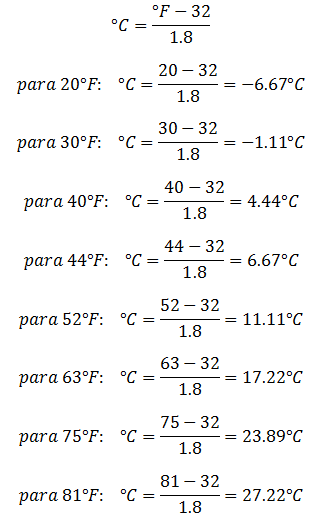
Conversion from Celsius to Kelvin and vice versa:
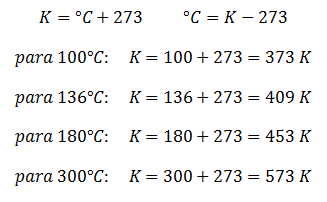
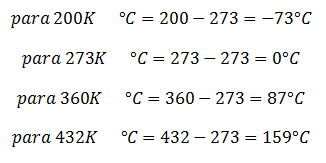
Conversion from Fahrenheit to Rankine and vice versa: