Concept in Definition ABC
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Dra. Maria de Andrade, CMDF 21528, MSDS 55658., on Aug. 2014
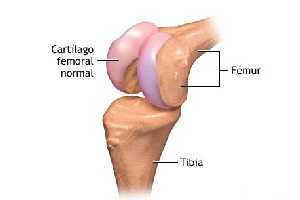 The Cartilage It is a tissue present in living beings of the animal kingdom whose function is to support some structures and organs, hence it is considered as a connective tissue.
The Cartilage It is a tissue present in living beings of the animal kingdom whose function is to support some structures and organs, hence it is considered as a connective tissue.
Cartilage is a semi-rigid tissue, its firmness allows it to resist mechanical stress but with greater flexibility than bone, which is a stiffer and harder tissue. These conditions are necessary in structures such as the ears where the pinna and external auditory canal are made up of cartilage, it also happens with the nasal septum and the wings of the nose, the trachea and the bronchi, all these structures although they have a certain degree of rigidity that make it maintain its shape, also have the ability to be moved by the action of the muscles that surround them, in the case of the road eastern air movement allows the bronchial tubes to be dilated or contracted.
Another structure where cartilage has a fundamental role is in the joints, there exists a special type of cartilage that is cartilage. articular, this covers the surface of the bones so that during movements they move smoothly without friction or friction, also absorbing forces like him
impact.The properties of cartilage are explained by its architecture At the microscopic level, this tissue is made up of a group of cells, known as chondrocytes, which are found surrounded by a matrix rich in collagen, where there are two substances that have the property of giving this tissue its great endurance in compression, they are chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid. These molecules have negative charges that make them constantly repel each other while attracting and holding a large amount of Water, this gives it a resistance that prevents the cartilage from being compressed, with aging and Repetitive microtrauma decreases the amount of these molecules and the cartilage becomes less resistant, giving rise so to the main disease degenerative apparatus locomotor that is Osteoarthritis.
Cartilage also has an important function and is that it allows the growth of long bones, as is the case of the bones of the arms and legs, in the childhood the union of the ends with the middle part of the bone is formed by the so-called growth plate that remains active until the end of adolescence when the increase in stature is ossified and stops, with which young people stop growing.
Topics in Cartilage