Definition of eukaryotic cell
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Cecilia Bembibre, in Mar. 2013
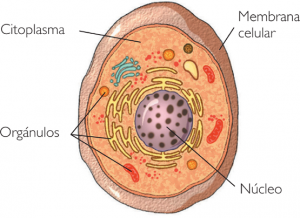 The name of cell Eukaryotic is one that applies to all cells of a living organism that have a membrane that covers and protects them from environment exterior, but especially for having a core mobile defined and delimited also within the cell by a protective layer or nuclear membrane. Eukaryotic cells differentiate from other types of cells such as prokaryotic cells in which the The nucleus also exists, but as it is not covered by any membrane or envelope, it is dispersed throughout the cell.
The name of cell Eukaryotic is one that applies to all cells of a living organism that have a membrane that covers and protects them from environment exterior, but especially for having a core mobile defined and delimited also within the cell by a protective layer or nuclear membrane. Eukaryotic cells differentiate from other types of cells such as prokaryotic cells in which the The nucleus also exists, but as it is not covered by any membrane or envelope, it is dispersed throughout the cell.
Eukaryotic cells are present in most of the living beings on the planet since their composition it allows us to talk from tiny beings to the world's most gigantic mammals and animals. All of them have this type of cells. In contrast, prokaryotic cells are only present in the organisms known as bacteria and arches, much simpler although they reproduce very easily. For specialists, the distinction millions of years ago between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells was one of the reasons why life became more complex and advanced.
Within the eukaryotic cell we find the cytoplasm, which is an emulsified liquid in which the different parts of the cell take place, including the nucleus. The cytoplasm is something like the placenta of a pregnant woman since without it the different elements of a cell could not survive. The plasma membrane will be the one that covers the whole of the cytoplasm and the other elements of a cell, protecting them and separating them from the external environment. In the cytoplasm we find the cell nucleus that is in turn covered by a membrane or nuclear envelope, which protects it and differentiates it from the rest of the parts of the cell.
The nucleus is the most important part of a cell since the material or information is housed there genetics what will make him living being Be that as it may and nothing else. This information is reproduced in the same way in all cells of the living being and will determine it from the moment of its birth until its death.
Topics in Eukaryotic Cell

