Concept in Definition ABC
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Cecilia Bembibre, in Jun. 2010
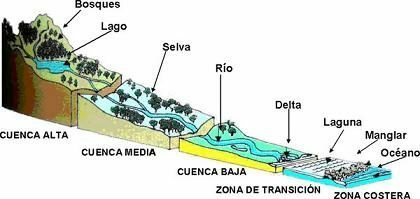 Basin is understood to be that depression or geographical shape that makes the territory lose height as you get closer to sea level. Watersheds are those that make the Water that comes from the mountains or the thaw, descends through the depression until it reaches the sea. In some cases, the basin may not reach sea level if it is a Valley enclosed by mountains, in which case the training aquifer will be a lagoon or lake.
Basin is understood to be that depression or geographical shape that makes the territory lose height as you get closer to sea level. Watersheds are those that make the Water that comes from the mountains or the thaw, descends through the depression until it reaches the sea. In some cases, the basin may not reach sea level if it is a Valley enclosed by mountains, in which case the training aquifer will be a lagoon or lake.
Watersheds can be divided into two main types: endorheic basins, those that do not reach the sea, resulting in the formation of stagnant water systems (such as lakes or lagoons); and the exorheic basins, those that do reach the sea and that therefore are not enclosed between the different sets of mountains. Normally, basins, whether endorheic or exorheic, can generate a large number of tributaries that all fall into the main watercourse, be it sea, ocean, lake or lagoon. At the same time, as these tributaries approach their final destination they lose their intensity original they had when they started their downhill course.
Watersheds are of great importance for the environment as well as for the human being. In this sense, they act as important reservoirs of water that can be used not only by humans for their consumption personal, different economic activities such as farming or navigation, but also for the consumption of animals and plants and therefore the development of complete and durable biotic systems.
It goes without saying that on planet Earth we find numerous hydrographic basins, each possessing particular characteristics. Some of the current seas are considered endoreic hydrographic basins due to the progressive loss of their contact with the ocean.
Topics in Cuenca


