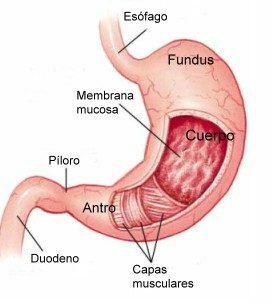
Concept in Definition ABC
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Javier Navarro, in Apr. 2015
 X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation of the same nature as radio waves, microwave waves, infrared rays, visible light, ultraviolet rays and light rays spectrum. The basic difference between X-rays and others lies in their origin, since X-rays arise from Extra-nuclear phenomena at the level of the electronic orbit and are produced by the deceleration of electrons.
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation of the same nature as radio waves, microwave waves, infrared rays, visible light, ultraviolet rays and light rays spectrum. The basic difference between X-rays and others lies in their origin, since X-rays arise from Extra-nuclear phenomena at the level of the electronic orbit and are produced by the deceleration of electrons.
The wavelength of X-rays is between ultraviolet radiation and gamma rays. X-rays are ionizing radiation, since by interacting with matter it causes the ionization of its atoms, that is, it creates charged particles.
The 3 key pillars that make up an X-ray equipment
An X-ray machine is made up of three fundamental elements: the X-ray generator, the tube, and the X-ray table. The generator is made up of a command that allows selecting a series of values (the kilovoltage or the exposition radiation), by a transformer that acts as an electrical supply (the voltage used ranges between 40 kv and 120 kv). The tube is made up of electrodes and an incandescent filament; X-rays being produced when electrons coming out at large
velocity They impact and create a beam of X-rays that are directed to an area of the patient's body and become a radiographic image.A little history
The history of X-rays begins with the experiments of the British William Crookes, who in the 19th century investigated the effects of certain gases when applying downloads of Energy.
 These experiments were carried out in an empty tube and electrodes to generate high voltage currents. When this tube, when it was near photographic plates, it generated some blurred images in them. This discovery was used by Nikola Tesla, who began to study this effect and already observed that there was a danger by exposing the organisms to radiation. For this reason, these rays were considered to have no practical utility.
These experiments were carried out in an empty tube and electrodes to generate high voltage currents. When this tube, when it was near photographic plates, it generated some blurred images in them. This discovery was used by Nikola Tesla, who began to study this effect and already observed that there was a danger by exposing the organisms to radiation. For this reason, these rays were considered to have no practical utility.
Despite this initial rejection, some French doctors began to use X-rays to look at the human body inside. From that moment on, radiology emerged as discipline medical.
At the beginning of the 20th century, the famous Madame Curie discovered radium and polonium, the chemicals involved in X-ray radiation.
X-Ray Themes