Concept in Definition ABC
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Dra. Maria de Andrade, CMDF 21528, MSDS 55658., in Jun. 2015
Chemical resonance
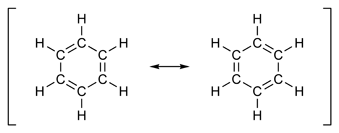 From the point of view of organic chemistry, the resonance is a tool that is used to carry out the formulation of molecules with double or triple bonds that can be represented by two or more Lewis structures in which the only existing difference is the distribution of electrons, these representations are called resonant structures.
From the point of view of organic chemistry, the resonance is a tool that is used to carry out the formulation of molecules with double or triple bonds that can be represented by two or more Lewis structures in which the only existing difference is the distribution of electrons, these representations are called resonant structures.
This method allows you to establish how you can stabilize the molecule by delocalization of its electrons which allows a greater approximation to its real structure, since many times a single Lewis structure fails to describe suitably a molecule so it is considered that the structure of a molecule can be represented by the mixture of all possible Lewis structures and not as a Balance between them.
When drawing the organic compounds that constitute resonance hybrids, it is not possible at any given moment to define the number of electrons on some of the atoms, which which leads to these compounds deserving a special nomenclature that consists of enclosing all the resonant structures between brackets.
It is considered that the greater the number of bonds, the greater the stability the resonant molecule will have; Energy of the molecule and the charge being more stable the one that has the negative charge in the most electronegative atom.
Two molecules that are clear examples of resonance are ozone and benzene.
Physical Resonance
Resonance, from the point of view of physical, is a phenomenon that occurs when a force external is capable of vibrating at the same frequency as a certain object, causing it to vibrate by increasing the amplitude of its movement which will result in a certain effect.
This is a phenomenon that occurs on a daily basis without us being aware of it many times, one of the main applications of resonance is The tuning of radio stations, which is achieved when the receiving device enters the same frequency as the signal emitted by the station.
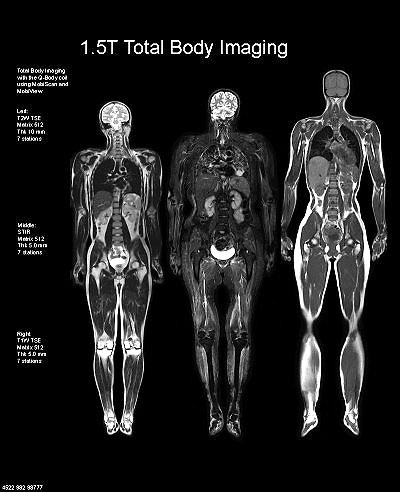 In the medical field by placing a patient in the field of a powerful electromagnet and sending a radio wave that resonates with the Hydrogen protons are achieved that they emit a signal that is captured to obtain an image of the patient that is known as Magnetic Resonance Nuclear.
In the medical field by placing a patient in the field of a powerful electromagnet and sending a radio wave that resonates with the Hydrogen protons are achieved that they emit a signal that is captured to obtain an image of the patient that is known as Magnetic Resonance Nuclear.
Other phenomena in which the resonance principle is applied is in the design of stringed instruments, in microwave ovens and even in the wireless electrical transmission discovered by Tesla.
Topics in Resonance