Concept in Definition ABC
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Dra. Maria de Andrade, CMDF 21528, MSDS 55658., in Jun. 2015
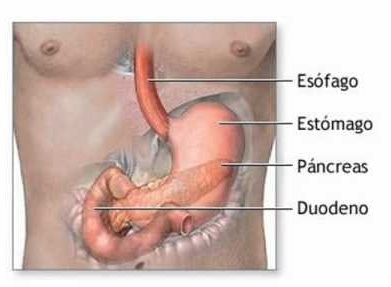 The Duodenum It is the first portion of the small intestine and covers the first 30 cm of it, it originates from the pylorus, which is the sphincter that controls the exit of the stomach and it continues with the jejunum.
The Duodenum It is the first portion of the small intestine and covers the first 30 cm of it, it originates from the pylorus, which is the sphincter that controls the exit of the stomach and it continues with the jejunum.
The duodenum is arranged in the shape of a horseshoe that hugs the head of the pancreas, it remains attached to the posterior wall of the abdomen, being located behind the peritoneum, this provision It gives rise to four portions called the first portion, second portion, third portion, and fourth portion of the duodenum.
Functions of the Duodenum
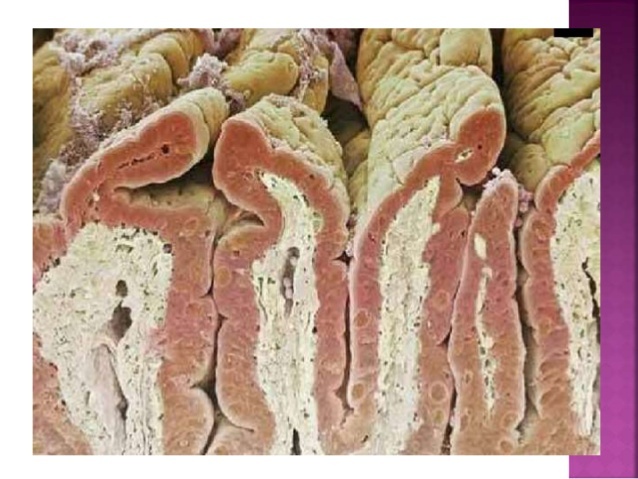
This segment of intestine has a series of folds in its internal or mucosa layer that give rise to villi that have the function of carrying out the absorption from nutrients coming from food during the digestion. It also contains structures called Brunner's glands that produce alkaline mucus that helps protect itself from the acidic content that reaches it from the stomach.
At the level of the second Procyon of the Duodenum, two important structures flow
The Choledocus.
This duct has the function of allowing the passage of bile that is produced in the liver and accumulates in the gallbladder towards the intestine, bile is necessary for the process of digestion of fats, the absorption of vitamins A, D, E and K, give its characteristic color to the stool, in addition to allowing the elimination of waste and substances metabolized by the liver.
The Wirsung duct.
It is the tube that carries secretions from the pancreas to the intestine, especially enzymes pancreatic diseases such as amylases, lipases and trypsinogens that are necessary to carry out the digestion of the carbohydrates, fats and protein respectively.
Main affections of the Duodenum
 This portion of the intestine can be the seat of various types of diseases, however among the frequent are:
This portion of the intestine can be the seat of various types of diseases, however among the frequent are:
Duodenal ulcer.
The duodenum can be affected by the acid secretion of the stomach which burns and erodes its surface until causing an ulcer, this is accompanied by pain especially after eating, nausea, vomiting and sometimes by stools with blood product of the hemorrhage with blood leakage into the intestine.
Giardiasis
Giardiasis is an infection caused by the parasite Giardia lamblia, this microorganism is capable of adhering to the villi of the duodenum preventing absorption processes from taking place intestinal leading to diarrhea and a failure to absorb nutrients that can lead to anemia and loss of weight.
Tumors The duodenum can also be the seat of primary tumors or be affected by the infiltration of neighboring tumors, especially pancreatic head cancer.
Topics in Duodenum