Definition of Theory of Everything
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Javier Navarro, in Jun. 2018
 In the field of theoretical physics, an attempt is made to understand the universe and for this, physicists resort to formulas math. One of the questions that arises is the following: how did the universe come about? This question is equivalent to asking how it all started and for this reason we talk about the theory of everything.
In the field of theoretical physics, an attempt is made to understand the universe and for this, physicists resort to formulas math. One of the questions that arises is the following: how did the universe come about? This question is equivalent to asking how it all started and for this reason we talk about the theory of everything.
The definitive mathematical formula that explains the origin of the universe does not yet exist.
Looking for the equation that explains the universe
One of the problems when it comes to finding an explanation for the universe is presented again in the form of a question: can human beings get to know the origin of the universe?
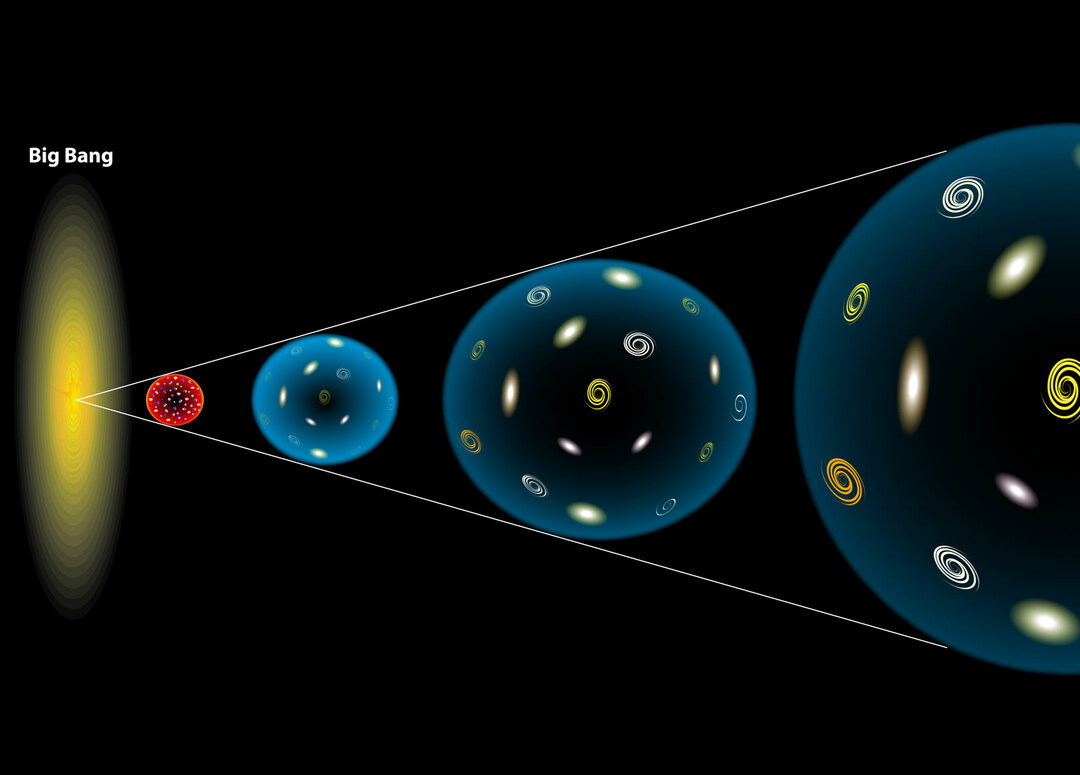
The fact of discovering the expansion of the universe from the explosion generated in the big-bang has been fundamental to understanding the origin of the universe, but such progress has not been translated into a mathematical formula concrete. In this sense, the formula of general relativity expressed by Albert Einstein states that where there is mass and Energy there is a distortion of space and time.
Einstein's advances on the relationship between mass, energy, and space-time were supplemented by another theoretical physicist, Stephen Hawking.
According to Hawking, the big bang is directly related to black holes. Thus, if it were possible to calculate the center of a black hole, it would also be possible to calculate the moment when the universe arose.
In the search for the Theory of Everything, some theoretical physicists propose to unify the theory of general relativity with the explanatory models of the most elementary particles, which are integrated in the field of physics quantum.
In other words, it is proposed to create an explanation that combines the micro-matter of the universe with space-time. This new course of theoretical physics was proposed by the Russian scientist autodidact Matvei Petrovich Bronstein. This scientist took as a reference some particles in microscopic space and tried to understand how the law of gravity intervened in such particles.
Came to the conclusion next: the microscopic world and gravity can be unified into one equation mathematics.
Superstring theory is the new paradigm of the Theory of Everything
According to the theory of superstrings, before the creation of the universe there was a world of elementary particles that were fluttering as if they were strings in movement.
East paradigm of theoretical physics proposes a new combination between elementary particles and the general theory of gravity. The search for a mathematical formula that explains everything implies understanding the smallest (the atoms) and the largest (the galaxies).
According to the proposal, both the matter and the energy of the universe are made up of a single element: tiny filaments of vibrating energy known as strings. This theory states that the particles into which atoms are divided (quarks) are made up of strings of oscillating energy that are similar to moving strings.
In other words, the type of movement of the strings is what generates the mass and the electric charge of the different particles. For this model to make sense, theoretical physics must contemplate a universe made up of ten dimensions and not all four. traditional, which means affirming that there are parallel universes that are in the same place as our universe, but in another dimension.
Photo: Fotolia - Designua
Topics in Theory of Everything
