Concept in Definition ABC
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Florencia Ucha, in Nov. 2011
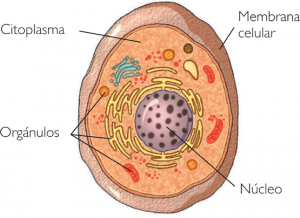 On biology, the word eukaryote is used to designate those cells that display their fundamental hereditary material or information genetics enclosed within a double membrane and have a cytoplasm organized. It is also known as eukaryote or eukaryote to the organism constituted by this type of cell.
On biology, the word eukaryote is used to designate those cells that display their fundamental hereditary material or information genetics enclosed within a double membrane and have a cytoplasm organized. It is also known as eukaryote or eukaryote to the organism constituted by this type of cell.
The main characteristic that eukaryotic cells observe is that they present their genetic information enclosed within the nuclear envelope, while the cytoplasm presents interconnected organelles whose limits have been set by membranes biological; the most conspicuous compartment of protoplasm is the nucleus.
On the other hand, eukaryotes usually present mitochondria that are membranous organelles that produce Energy, although, it should be noted, that some protist-type eukaryotes no longer present mitochondria after the normal course of their evolution.
On the other hand, the presence of plastids in the cytoplasm makes it easier for certain eukaryotes to carry out the photosynthesis.
Although there is an important variety of eukaryotes, which would suggest a diversification, such a situation is not such, but on the contrary, despite the variety, these cells share the same biochemical composition and a metabolism homogeneous. The aforementioned is the main difference that eukaryotes present with respect to prokaryotes, those cells whose genetic material is distributed in various organelles.
And on the other hand, the organisms Eukaryotes make up the Eukarya domain, which includes organisms from all four kingdoms, that is, plants, fungi, protists, and animals.. A revealing finding in this regard is that most of the now extinct organisms, which have been studied by paleontologists, belonged to this domain.
Eukaryotes reproduce by dividing asexual, in a process called mitosis and generally through processes of reproduction based on meiosis. Furthermore, eukaryotic reproduction involves alternation between generations. haploid (organism whose cells have the number of chromosomes reduced to one series instead of two, as in normal somatic cells) and diploid (organism that has double endowments of chromosomes).
Themes in Eucariota
