Concept in Definition ABC
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Dra. Maria de Andrade, CMDF 21528, MSDS 55658., on Apr. 2015
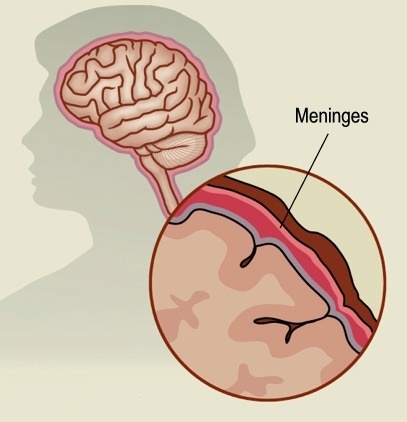 The Meninges are three membranes that line and protect the brain and spinal cord, structures that make up the Central Nervous SystemThey are the Pia mater, Arachnoid, and Dura mater.
The Meninges are three membranes that line and protect the brain and spinal cord, structures that make up the Central Nervous SystemThey are the Pia mater, Arachnoid, and Dura mater.
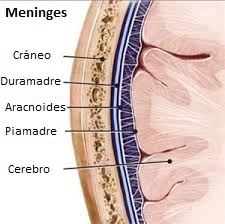
The pia mater is the innermost membrane, she completely covers the nervous system central and is in direct relationship with the blood vessels.
The Arachnoid is located outside it, it is formed by a membrane that emits extensions towards the Pia mater which gives rise to a cavity inside, the subarachnoid space, through which the Liquid flows Cerebrospinal.
The Dura mater is the outermost membrane, it has a fibrous structure and a pearly white color, it separates the central nervous system from the skull and the spinal canal from the vertebral column. Between the Dura and the Arachnoid there is a virtual space known as the subdural space. At the level of the skull, the Dura mater is directly attached to the bone, whereas in the spine there is a space between this membrane and the walls of the spinal canal called the Epidural space.
Inside the skull there are no veins as such, but venous sinuses, they are drainage structures that are formed by the Dura mater. This membrane also forms a structure known as the Tentorio or Tent of the Cerebellum, a prolongation of the Dura mater that forms a septum that completely separates the cerebellum from the brain.
Meninges Disorders
 The meninges are the seat of a series of disorders, among which three stand out predominantly for their importance and frequency.
The meninges are the seat of a series of disorders, among which three stand out predominantly for their importance and frequency.
Meningitis
It is the colonization of the meninges by pathogenic germs, mainly viruses and bacteria, it is an infection that occurs frequently in the childhood; it is accompanied by discomforts such as headache, fever, and a stiff neck. His evolution It is variable, being able to recover completely or leave sequelae which will depend on factors as the microorganism that produces it and the conditions of the patient's immune system.
Meningioma
It is a tumor that affects the Dura mater membrane, although it is not a malignant lesion per se, it is capable of causing a series of product symptoms. compression of neighboring structures which will produce a series of symptoms that may include headache, paralysis, loss of the force, loss of sensitivity, cranial nerve involvement, dizziness and seizures among others.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
The rupture of a blood vessel in the brain can cause bleeding into the subarachnoid space, this occurs mainly in the case of aneurysms or an arteriovenous malformation and is manifested by a severe and very severe headache of sudden onset that may be accompanied by disorders of the conscience, vomiting, stiff neck and seizures.
Topics in Meninges