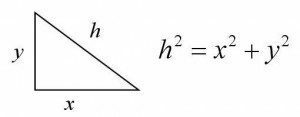Concept in Definition ABC
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
By Dra. Maria de Andrade, CMDF 21528, MSDS 55658., on Feb. 2015
 The Mitochondria It is a structure that is part of cells, where it fulfills important functions related to the cellular respiration and the production of Energy.
The Mitochondria It is a structure that is part of cells, where it fulfills important functions related to the cellular respiration and the production of Energy.
The body's energy is obtained from the breakdown of glucose molecules, a process that begins in the cytoplasm but that runs largely and is completed in the mitochondria. Each molecule of this sugar will undergo a series of chemical changes that produce CO2 (carbon dioxide) and a molecule known as ATP (adenosine triphosphate) which is the way in which energy is stored in the body.
ATP is essential for the different processes of the body to take place. Every time energy is required to carry out a certain function, ATP is converted into ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and the latter into AMP (adenosine monophosphate); The energy comes from the release of each phosphate group that the molecule contains, once it has released them it recharges them in the mitochondria in a complex multi-step process.
Initially, a process known as the Krebs Cycle occurs, there each molecule of glucose is degraded to produce 2 molecules of ATP, 6 molecules of NADH and two molecules of FADH2, then these last two molecules, NADH and FADH, go to a stage called the respiratory chain or chain of transport of electrons, where the participating molecules carry out the process of transporting electrons along a second cycle through several molecules, until these finally bind to oxygen and hydrogen ions to form Water. As the electrons pass through the respiratory chain, they release energy that is used to produce more ATP molecules.
In this way we have that in the organisms aerobics, as in our case, the food and oxygen are necessary to produce energy, the end product of this process being CO2 and water. Approximately 90% of all ATP is produced in this way, the remaining 10% is obtained by metabolism anaerobic.
At the end of the whole process, a molecule of glucose will lead to the production of about 38 molecules of ATP, other molecules obtained from the feeding They also end up in the Krebs cycle and in the respiratory chain, entering through other metabolic routes, such is the case of other forms of sugars, fats and protein.
Topics in Mitochondria