How are Acids, Bases and Salts formed?
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
There are several theories to define the acids and the bases, among which are the Arrhenius, the Brönsted-Lowry and the Lewis.
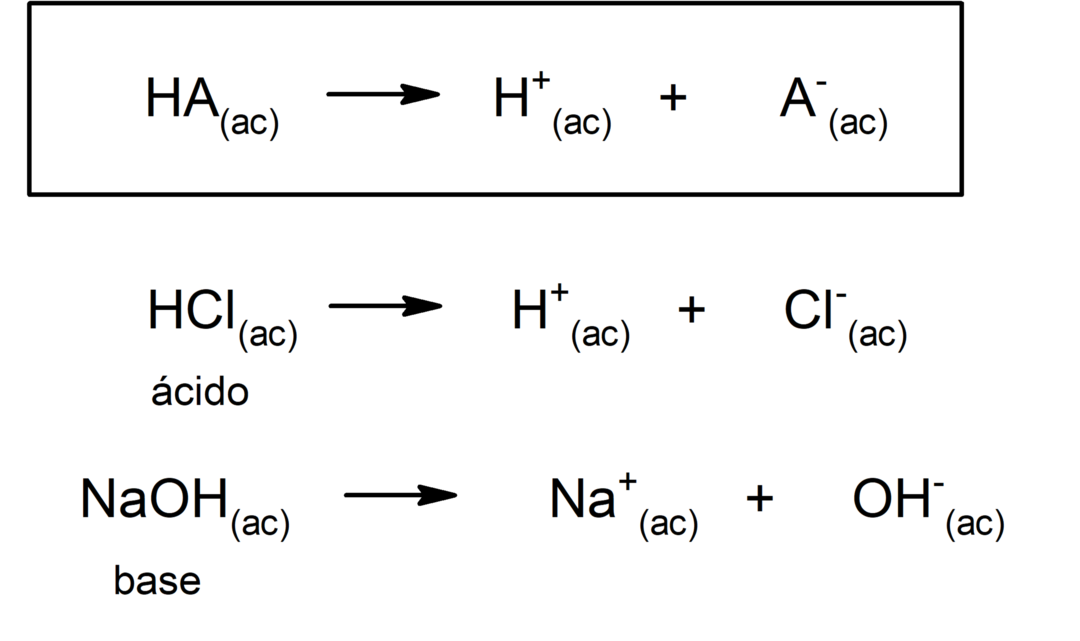
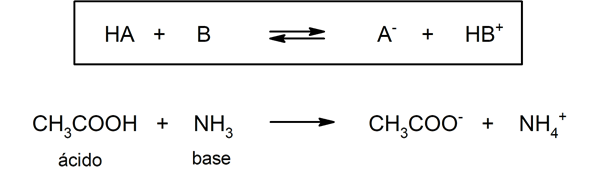
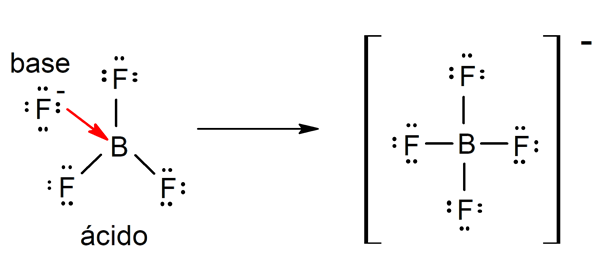
Type acids oxacids are usually formed by reaction between a non-metallic oxide with water, while acids of the type hydracids are formed by the combination of a non-metal with hydrogen in aqueous solution. For example:sulfuric acid (H2SW4) it is an oxacid and hydrochloric acid (HCl(ac)) it's a hydracid.
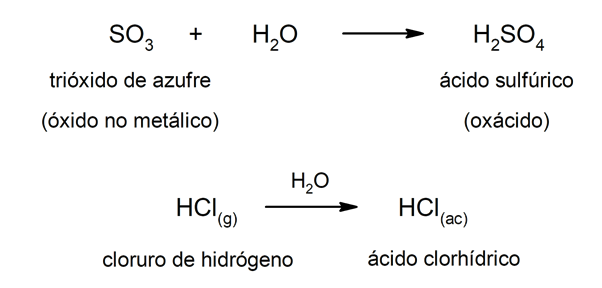
On the other hand, bases can be formed as a result of the reaction between a metallic oxide And the water. For example: magnesium hydroxide (Mg (OH)2).
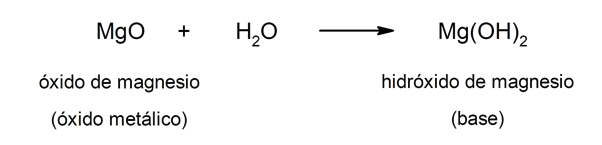
General characteristics of acids and bases
In general, acids are sour and corrosive. The bases are also corrosive, bitter in taste, caustic when in contact with the skin and have a soapy touch. On the other hand, acid solutions have a pH less than 7, while base solutions have a pH greater than 7.
Acid and base strength
The tendency of an acid to dissociate and lower the pH is often referred to as "acid strength." An acid is strong when it can fully dissociate in aqueous solution and is weak when its dissociation occurs partially. Examples of strong acids are perchloric (HClO
4), sulfuric (H2SW4), hydroiodic (HI), hydrobromic (HBr), hydrochloric (HCl) and nitric (HNO3). On the other hand, acetic acid (CH3COOH), citrus (C6H8OR7) and benzoic (C6H5COOH) are weak.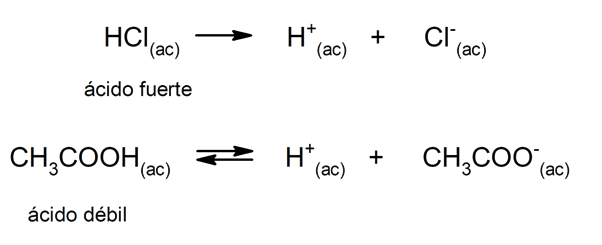
Similarly, they can be considered as strong bases those that dissociate completely in aqueous solution, and weak when their dissociation occurs partially. Examples of strong bases are potassium hydroxide (KOH), sodium (NaOH), lithium (LiOH) and magnesium (Mg (OH)2). On the other hand, ammonia (NH3) is a weak base.
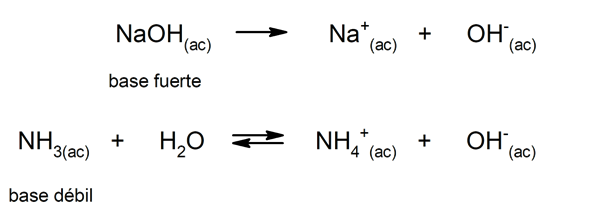
How are salts formed?
The you go out are ionic compounds of varying complexity, abundant in nature and generally formed by the combination of acids with bases in a neutralization reaction, which generates a release of Water. They can also be formed as a result of the reaction between a metal and an acid, a metal and a nonmetal, or the reaction between different salts.
The salts can be classified into:
Distribution and importance
Acids are extremely important both in industry like in the nature. For example, hydrochloric acid is part of our digestive system and is necessary for us to degrade the nutritional compounds present in food. Deoxyribonucleic acid, better known as DNA, makes up chromosomes, which is where the genetic information necessary for them to be encoded is encoded. living beings multiply and develop. Boric acid is a prominent component in the glass industry.
The calcium carbonate It is a very abundant salt in various types of limestone rocks. By high share temperatures (900 ° C) from calcium carbonate, calcium oxide or quicklime is obtained. Adding water to quicklime produces calcium hydroxide, called slaked lime, which is a base. These materials they are used in construction.
Follow with:



