20 Examples of Chemical Phenomena
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
The chemical phenomena (or chemical reactions) are those phenomena in which changes occur in matter, and new substances called "products" are formed, and other called "reactants" decompose. For example: wood rot, paper burning, composting.
Chemical reactions can be spontaneous (reactions that occur without the need for energy or catalysts) or not spontaneous (reactions that need the contribution of energy, catalysts or some external intervention to occur). Many times, for a reaction to occur it is necessary for the reagents to have a temperature specific, a pH a set pressure value, etc.
It may also be essential to control the velocity to which chemical reactions occur. The catalysts They are substances that are added to a chemical reaction to increase its speed, while inhibitors are substances that slow down the speed of chemical reactions. Other factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction are temperature, pressure, the concentration of reactants, and the nature of the reaction itself.
It can serve you:
Types of chemical phenomena
Chemical reactions can be:
Inorganic reactions. Intervene inorganic compounds and can be classified according to:
- The sense in which the reaction occurs.
-
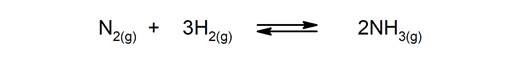
Reversible reactions. They occur both ways, so the products can break down and form the reactants again.
-
Irreversible reactions. They only happen one way.

-
Reversible reactions. They occur both ways, so the products can break down and form the reactants again.
- The type of particle that reacts.
-
Acid-base reactions. H ion transfer occurs+.

-
Oxidation-reduction reactions. One of the reactants oxidizes (increases its number of oxidation), while the other is reduced (its oxidation number decreases). In these reactions electron transfer occurs.

-
Acid-base reactions. H ion transfer occurs+.
- The rate of reaction.
-
Quick reactions. They occur in a very short time.
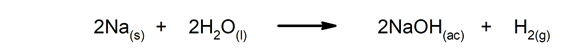
-
Slow reactions They take a long time to complete.
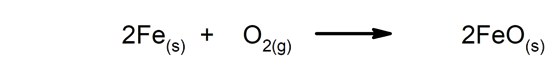
-
Quick reactions. They occur in a very short time.
- The form of the energy it emits or absorbs.
-
Exothermic reactions. As they occur, they release heat.
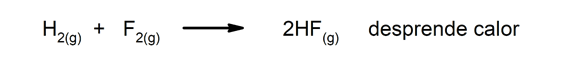
-
Endothermic reactions. When they occur, they absorb heat.

-
Exoluminous reactions. When they occur, they emit light.

-
Endoluminous reactions. To happen, they need light.
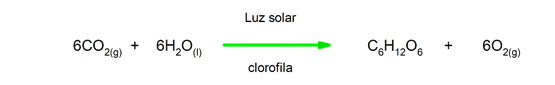
-
Exothermic reactions. As they occur, they release heat.
- The type of transformation.
-
Synthesis or addition reactions. Two substances combine to form a new substance.
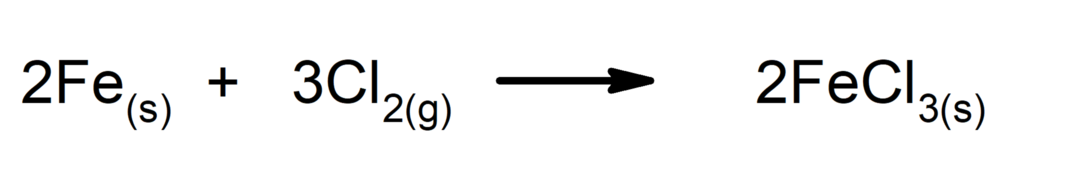
-
Decomposition reactions. One or more substances break down into their simplest constituents.
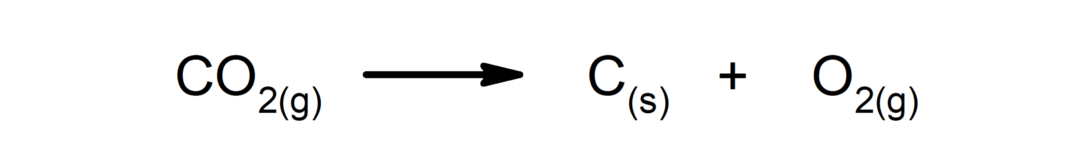
-
Displacement or substitution reactions. One element or compound replaces another in a compound, releasing it.
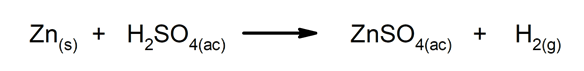
-
Double substitution reactions. Two compounds exchange elements or compounds at the same time.

-
Synthesis or addition reactions. Two substances combine to form a new substance.
Organic reactions. They are reactions in which organic compounds intervene. They have many classifications based on the type of organic compound that reacts and the type of reaction that it undergoes. Some examples are:
-
Halogenation of alkanes. A hydrogen is substituted for a alkane by a halogen.
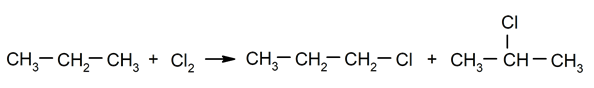
-
Combustion of alkanes. An alkane reacts with oxygen to generate carbon dioxide and water, if combustion is complete.
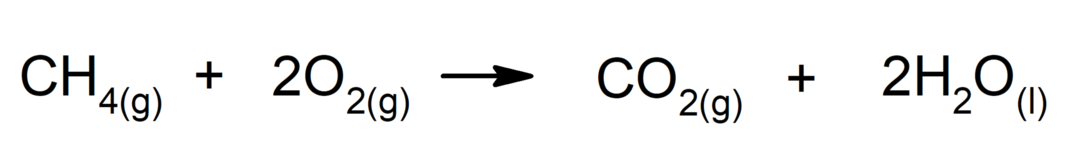
-
Halogenation of alkenes. Halogens are substituted for one or both hydrogens of the carbons that are involved in the double bond.
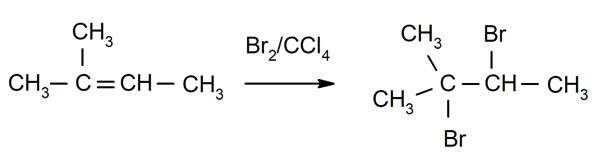
-
Hydrogenation of alkenes. Hydrogens are added to the carbons involved in the double bond to form the corresponding alkane.
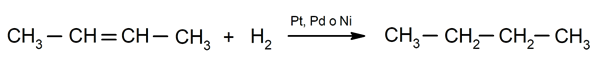
Importance of chemical phenomena
Many chemical phenomena sustain life of living things, such as digestion in humans and animals, photosynthesis in plants and respiration in both.
Another very important chemical process, especially in the life of microorganisms, is the fermentation, which is usually used in the manufacture of food like cheeses, yogurts, wines and beers.
All the increase and the growth of a living being It involves chemical reactions that take place in it, sometimes stimulated by certain environmental conditions.
Examples of chemical phenomena
Around us there are numerous cases of chemical phenomena or processes that include them:
- Wood rot
- Combustion of paper
- Resistance to antibiotics bacteria
- Milk that turns sour
- Disinfecting a wound with alcohol
- Using fruit salt to fight heartburn
- Burning a candle
- Blood clotting
- Muscle fatigue after intense exercise
- Death of insects by insecticides
- Obtaining Roquefort cheese
- Obtaining cider
- Obtaining yogurt
- Composting
- Ensilage
- Obtaining bioethanol from molasses
- Swollen tin cans
- Rotten egg
- Rusting of a grate
- Obtaining biodiesel from palm oil
Chemical phenomena in industry
Certain chemical phenomena are also key in theindustry. To begin with, the combustion of hydrocarbons (such as gasoline, diesel or kerosene) produces Energy to run the machines that handle countless industrial processes.
On the other hand, the steel industry, paper, plastics, construction materials, paints, drugs, products for the agro, etc., are based on various chemical phenomena such as galvanization, electrolysis and many others more.
The generation of new energy sources (like biodiesel and bioethanol) is also based on this type of phenomenon.
The transformation of energy
In chemical phenomena it is common for there to be energy transformation. For example, when the chemical energy contained in the bonds of a certain molecule is transformed into electrical energy or released as heat (this occurs in exothermic phenomena, such as when hydrochloric acid is mixed with zinc), there is a transformation of Energy. The same happens when light energy is captured and transformed into chemical energy.
Some chemical processes require heat to run and are called "endothermic." Others require the presence of catalysts or cofactors.



