15 Examples of Diffusion and Osmosis
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
The diffusion and osmosis they are processes of passive transport (they do not require extra energy to occur, contrary to active transport) of particles of one or more substances found in different concentrations of solute and they are put in contact with each other, either through a semi-permeable membrane (particular case of osmosis) or some other means.
What is broadcasting?
Diffusion is a physical process which is based on the flow of particles of a substance from an area of high concentration of solute towards a low concentration, until the concentration is approximately the same in both zones. The motion of the particles is based on their Kinetic energyIn other words, there is no external energy input for diffusion to occur. For example: the passage of oxygen in the pulmonary alveoli.
This movement occurs in any of the aggregation states of the matter, but it is more easily observed in the case of liquids and gases. The tendency of the movement is towards the formation of a mix uniform of the two types of particles.
The scientist Adolf fick He established in 1855 some laws that bear his name, and describe various cases of the diffusion of matter in a medium in which initially there is no equilibrium. These laws relate the density of the flow of the particles with the difference in concentration between the two separate media, its coefficient diffusion and permeability of the membrane (in case the separating medium is a membrane semipermeable).
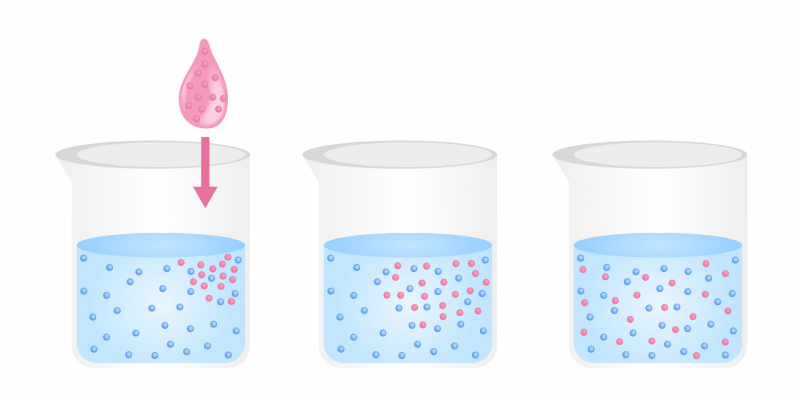
Examples of diffusion
- The passage of oxygen in the pulmonary alveoli.
- Nerve impulses, which involve ions sodium and potassium across the membrane of the axons.
- If you take a diffuser pair consisting of two metals brought into contact through their faces, are heated above fusion and then they cool down, it will be verified that the composition has changed: diffusion of nickel atoms towards copper and vice versa occurred.
- The warming and color change of a cup of coffee when a good proportion of cold milk is added.
- The entry of glucose to red blood cells, coming from the intestine.
- In an estuary, there is a less dense diffusion of river water that flows over the water of sea.
- If you put a tablespoon of sugar in a glass of water, the molecules of sucrose diffuse through the water.
- The diffusion of gases can be seen when a perfumed person enters a closed place, and everyone immediately senses the smell. The same happens when someone smokes indoors.
What is osmosis?
Osmosis constitutes a type of diffusion, but with two particular characteristics:
In this way, it is observed that the solvent tends to pass through the membrane in the direction of the dissolution whose concentration is higher, which ends up producing an increase in the amount of solvent in the most concentrated part (in solute) and decrease in the less concentrated part (in solute), that is, the solvent moves from the area with the lowest concentration in solute to the area with the highest concentration in solute. This is a process that is repeated until the concentration (both solute and solvent) of the solution is equal on both sides of the membrane.
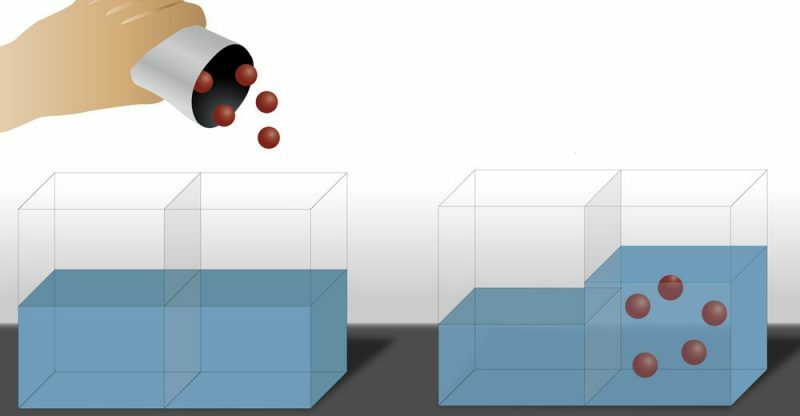
There is also the Inverse osmosis, where the passage of the solvent occurs in the opposite direction than conventional osmosis, that is, the solvent moves from the solution more concentrated in solute to the less concentrated in solute. To achieve this, pressure is applied to the solution more concentrated in solute.
Because it is important?
The solubility of the solute in the solvent and the nature of the semi-permeable membrane to be used are the fundamental factors that determine the effectiveness of the osmotic process: one of the factors that influences the so-called ‘solubility’ are the interactions between the components of the dissolution.
The osmotic process It is essential in biological processes where water is the solvent, especially in those processes aimed at maintaining the water and electrolyte balance in the living beings, regulating water levels in the cell or in the body in general: without this process, there could be no regulation of liquids and absorption of nutrients.
Examples of the osmosis process
- Living beings unicellular living in fresh water enter large amounts of water.
- The absorption of water by the roots in plant organisms, which allows growth.
- Obtaining water from the epithelial cells by the large intestine.
- Split a potato, placing a little sugar with water on one end and a plate with water on the other. The potato acts as a membrane, and after a while it will be seen that the solution that has sugar now has more liquid.
- The hormone ADH that allows the reabsorption of water by the collecting duct in the kidneys.
- The elimination of very dilute urine whereby the fish expel the maximum liquid with the minimum loss of you go out.
- The elimination of water through sweat in people.
- Filters to purify water work with reverse osmosis, since they are made with a material that allows the passage of water, but not of larger molecules.
Follow with:
