15 Examples of Agricultural Activities
Miscellanea / / July 04, 2021
Is named agricultural sector to a part of the primary production sector of the companies whose economic activities, commonly rural or linked to extra-urban life, point to the exploitation of resources from the agricultural sector (farming) and livestock (cattle raising) mainly. According to the legislation of the countries, fish farming can also be part of this sector. For example: vegetable cultivation, floriculture, pig farming, beekeeping.
These activities provide raw material to a long part of the commercial chain, such as the food industry, furriers, restaurants, urban markets, seasonal commerce and a long etcetera, especially in those sectors related to food handling and leather treatment (shoes, gloves, etc.).
Due to their means of operation, these activities are strongly conditioned by climatic conditions, the quality of the soils and the introduction of technological advances of a different nature that enhance their productivity or seek to compensate for environmental weaknesses inescapable.
Similarly, they are vulnerable to environmental pollution and the effects of climate change, so they represent a vulnerable sector in the face of the growing and unstoppable demand for food on a global scale.
On the other hand, in less developed countries the agricultural sector is usually located in populations poor or devoid of services, which affects the quality of life of its producers and promotes an unmanageable exodus to the city.
Examples of agricultural activities

- Grain cultivation, cereals and oilseeds. One of the commercial sectors that generates and displaces the most volume of merchandise worldwide is that of seeds, cereals and grains. Both for food, to nurture other crops or introduce bioengineered seeds, for not talk about wheat, rice and corn, cornerstones of the diet of the five continents, this sector of the industry it is perhaps the most robust of the agricultural area as a whole.
- Cultivation of vegetables. Large-scale vegetable production is the main food injection available in urban or suburban markets around the world. So much so is his demand, which are often cultivated in artisanal and organic ways, avoiding the effects of pesticides and pesticides.
- Fruit crops. Usually linked to seasonal fruit, these sectors have large areas of cultivation in which production takes place on a massive scale. According to the distribution channels chosen, these fruits may go to the ordinary market network or they can even be sold in trucks that travel the streets, especially when they come from small farmers. A high percentage also goes to urban industries and manufacturers, which make elaborate desserts and non-perishable consumer goods with them.
- Greenhouse and nursery crops. Usually on a smaller scale, since they are crops that do not require large areas of land but rather apply the laws of agriculture intensive in limited spaces but with high performance, they tend to produce a wide variety of vegetables and legumes that supply the demand local. Many of these minor crops are organoponic in form, and unlike traditional ones, they can take place within cities.
- Floriculture. The cultivation of flowers for personal consumption or for the production of Navets and arrangements is also an important industry in the field, especially in countries such as Colombia and Mexico, where they contribute a not inconsiderable sector of the economy local from various cities.
- Forestry. This is the name given to the care and cultivation of wild vegetation, in woods, hills or mountains, allowing the extraction of materials (wood, cork, rubber) through a more or less considerable industrial intervention, without involving the transformation of the natural space into a farm or cultivation area. Many of the materials that feed the light manufacturing industry come from these types of crops.
- Bovine livestock. Undoubtedly the most popular and widespread livestock activity of human civilization, whose origins date back to remote antiquity and whose importance in most of the Western gastronomies is undoubted, not only for its meat contribution, but also for dairy derivatives and a whole culture of exploitation of leathers for clothing and Utensils.
- Pig farming. The pig occupies the second place in importance in the western livestock activity, since its meat is generously incorporated into the various diets of the hemisphere, both in sausages, cutlets and very diverse preparations that benefit practically the entire body of the animal. In addition, their exploitation is relatively inexpensive, since instead of feed, at least in small-scale livestock, they are usually supplied with surplus food and organic material of waste.
- Poultry farming. The raising and slaughter of chickens is also an extremely central economic activity in the livestock sector. Its meat is appreciated almost universally, as well as those prepared from eggs, which allows a high profitability for the producer. However, it has often been questioned for the use of hormones and other genetic supplements that are unethical and in the long run undermine the consumption of this white meat.
- Sheep and goat farming. Less widespread in comparison, and yet popular in Arab countries, Europe, and Patagonia Argentina, sheep and lamb grazing also had their place in rural development and in the imaginary collective. The raising and slaughter of goats and rams is also appreciated, although not as central as cattle or pigs.
- Livestock of camelids. The llama, the vicuña and the guanaco are American camelids whose grazing occurs in the South American regions of Argentina, Peru, Bolivia and Chile. Its meat is usable, as well as its milk, and its fur is a source of fabrics of various invoices (gloves, scarves, coats), which are priced at a good price in the cities.
- Other forms of livestock. There are other forms of livestock adapted to the diversity of regions inhabited by man, usable as a source direct and indirect food and that would also enter the agricultural sector, by individuals or exotics that may seem.
- Livestock support activities. The activities of the branch are also part of the agricultural sector, such as the preparation of feed to feed the animals, distribution, slaughter or different secondary forms of exploitation that, however, take place in rural areas or, at most, in intermediate segments of the production chain.
- Fish farming and fish farms. Depending on the legislation, this item may belong to the agricultural sector or coastal fishing. However, captive breeding of gastronomically valued species such as trout, occurs in a way that is not very similar to the coastal collection of Marine species, and that is why it is closer to the livestock sector than to fishing.
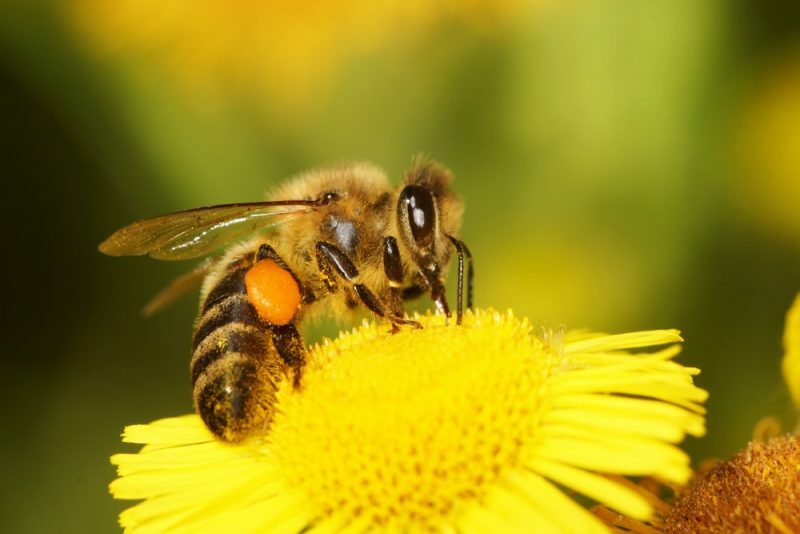
- Beekeeping and honey gathering. The breeding and maintenance of bee hives for extraction and collection of products of various types is also a well-known item in the agricultural sector. In this way, honey, royal jelly, wax, pollen, propolis and apitoxins are obtained, all of popular consumption and even pharmaceutical evaluation. Since the 1980s, however, there has been an alarming decrease in bees worldwide, which has been studied extensively by experts in the field, given the importance of these insects in pollination.

Follow with: