Definition of Lymphatic System
Miscellanea / / November 13, 2021
By Dra. Maria de Andrade, CMDF 21528, MSDS 55658., on Nov. 2015
 The lymphatic system is an important part of circulatory system, is made up of lymph nodes, lymphoid organs and a network of ducts that connect these structures with each other and with the general circulation known as lymphatic vessels.
The lymphatic system is an important part of circulatory system, is made up of lymph nodes, lymphoid organs and a network of ducts that connect these structures with each other and with the general circulation known as lymphatic vessels.
This system is located throughout the body, except at the level of the Central Nervous System, It is also directly related to the immune system or defense system of the body.
Lymphatic circulation
The lymphatic system intervenes in the processes of collecting fluids and various substances that are deposited or stored in tissues, as well as transporting cells of the immune system to the sites where they are required.
The drainage function of the lymphatic system allows the accumulated fluids in the tissues as a result of the inflammatory response, trauma, infectious process or venous insufficiency are taken back into the venous circulation to be filtered by the kidney and finally eliminated with the urine.
The fluid contained within the lymphatic system is known as lymph, it is yellowish in color similar to blood plasma, it is made up of Water, protein and cells of the immune system such as lymphocytes, which are a type of white blood cell.
Lymphatic structures
Lymph nodes Along the path of the lymphatic vessels are located a series of nodes known as lymph nodes, these constitute a kind of filters and tend to be distributed forming groups that are located mainly at the level of the neck, armpits, groin and inside the abdomen along the great vessels such as the aorta artery and the vein digging. Lymph nodes are recognized for microorganisms like viruses and bacteria starting the activation of B lymphocytes that are a type of white blood cell responsible for manufacturing antibodies, for this reason the lymph nodes increase in size when a infection.
Tonsils Lymphatic tissue is located at strategic points in the apparatus digestive system, at the level of the oral cavity they are found at the beginning of the pharynx, in structures known as the tonsils and adenoids, there is also lymphatic tissue in the cecal appendix, this strategic location allows to have a defense tissue in two important entry points of germs to the organism such as the airway and the mouth.
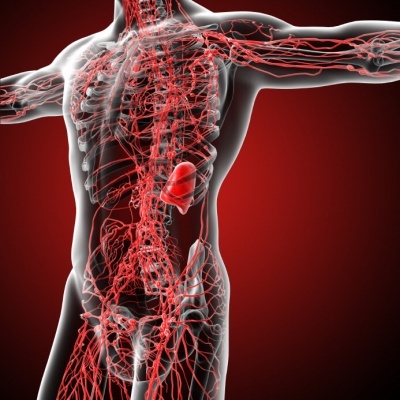 Scam In the embryonic stage and during childhood great immunological activity occurs in the thymus, an organ located behind the sternum, which is related to the maturation of T lymphocytes, which are a type of white blood cell responsible for recognizing the cells of the body and differentiate them from foreign cells as well as coordinate the response of the defense system against microorganisms.
Scam In the embryonic stage and during childhood great immunological activity occurs in the thymus, an organ located behind the sternum, which is related to the maturation of T lymphocytes, which are a type of white blood cell responsible for recognizing the cells of the body and differentiate them from foreign cells as well as coordinate the response of the defense system against microorganisms.
Spleen. It is an organ located inside the abdomen, on the left side of it, its main function is the elimination of aging blood cells as well as acting as a reservoir or reservoir of blood. The spleen also plays an important role as a lymphatic organ, it acts as a filter that collects the different antigens (substances foreign to the body) being able to produce immunoglobulins and substances necessary for the cells of the defense system to be able to eliminate bacteria that are protected by a capsule, such as pneumococcus, a bacterium that causes diseases such as pneumonia.
Photos: iStock - SomkiatFakmee
Topics in Lymphatic System