Definition of Nitrogen Cycle
Miscellanea / / November 13, 2021
By Florencia Ucha, in Dec. 2013
 Nitrogen it's a chemical elementof non-metallic characteristics, colorless, gaseous, odorless and transparent, which has been present in a very high percentage in the air. It is symbolized by the letter N capital letter, while its atomic number is the number 7.
Nitrogen it's a chemical elementof non-metallic characteristics, colorless, gaseous, odorless and transparent, which has been present in a very high percentage in the air. It is symbolized by the letter N capital letter, while its atomic number is the number 7.
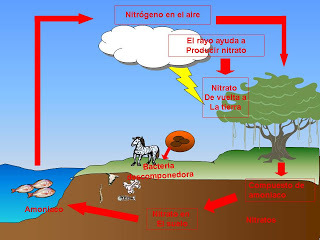
Meanwhile, it is called as nitrogen cycle to each of the processes, whether abiotic and biological, from which this element is supplied to living beings; formally it is a biogeochemical cycle and it consists of the movement of this element, or of others such as carbon, oxygen, calcium, hydrogen, sulfur, potassium, phosphorus, among the environment and the living being.
Thanks to this process the Balance dynamic in terms of composition of the terrestrial biosphere.
It should be noted that living beings have a significant amount of nitrogen in their chemical composition. They receive the oxidized nitrogen through salts (nitrate) and transform it into amino acids, the most common being those that are integrated in the
protein.Meanwhile, for nitrate to be present again, it is necessary to intervention from organisms to extract it from the biomass and return it in the reduced form of ammonium ion.
However, as ammonium and nitrate are very soluble substances that the current and infiltration very easily carry them towards the sea. It would not be possible for this element after its conversion to remain at atmospheric level, then, the oceans would be very rich in terms of nitrogen and the most continental masses, unfortunately, would not have this chemical element as important for life as we have already viewed.
However, there are two other processes that allow the continents not to become biological deserts as a consequence of the lack of nitrogen and these are: nitrogen fixation and denitrification. It is worth noting that both processes are reciprocally symmetric.
In nitrogen fixation, soluble compounds are generated from atmospheric nitrogen, while denitrification, which is a way of breathing anaerobic, it will return nitrogen to the atmosphere.
Thanks to these two processes it is possible to maintain a remarkable nitrogen deposit in the air, representing 78% of the volume.


