Concept in Definition ABC
Miscellanea / / December 09, 2021
Conceptual definition
Hydrolysis is understood to be any reaction of water with a substance that produces a displacement of the ionization balance of the water.

Chemical engineer
The phenomenon occurs, for example, when a salt dissolves in Water, where the salt, which is an electrolyte, is completely ionized and, when reacting with water, can form hydroxyl or hydronium. From the dissociation of the salt, the pH of a dissolution knowing that the higher the character acid or basic of the compound, the lower the hydrolysis effect.
Strong and weak acids
Let's consider a typical example such as HCl, it is a strong acid that when ionized behaves as follows:
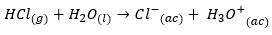
To study the effect of hydrolysis we focus on the conjugate base: C {l ^ -} {(ac)}, this anion is a weak conjugate base, that is, it has a weak tendency to take a proton out of water to form a hydroxide. Whereas, if we think of a weak acid, for example:
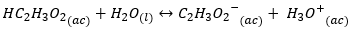
Its conjugate base C_2 {{H_3O_2} ^ -} _ {(ac)} \ will have a strong basic character, this will lead to the formation of hydroxide:
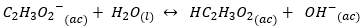
East Balance is shifted towards the direct direction of the reaction, to the right and, as a consequence, this anion has a high capacity to influence pH through production hydroxyl. While in the case of Cl-, there is no influence on the pH of the solution.
If the conjugate base, the anion, is a species capable of capturing protons from water, then the pH of the solution increases due to the formation of OH-.
Strong and weak bases
Let us now look at the case of strong or weak bases that partially or completely ionize in water and may or may not influence the pH of the solution.
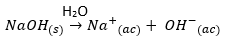
If we take {{Na} ^ +} {(ac)}, a small cation, a weak acid, it will not influence the pH of a solution, since it is not capable of donating protons to water. As long as:
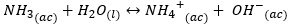
The cation {{NH_4} ^ +} {(ac)} is a strong acid, which comes from a weak base (ammonia). Therefore, it has the ability to donate a proton to the water (hydrolyze) as follows:
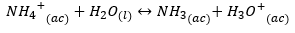
This explains why the dissolution of ammonia in water lowers the pH, given the formation of hydroniums. In this case, the displacement equilibrium is to the right.
Dissolution of salts
Just as we saw the effect of cations and anions separately, when they dissolve you go out in water both effects are combined and, depending on the relative capacity of the ions to react with water, the formation of hydroxyl hydroxyls will prevail over hydroniums or vice versa.
To understand it better, we will work with some cases:
- If we dissolve table salt in water, in solution We will have Na + cations and Cl- anions. As we saw previously, both species have little ability to react with water, therefore, neither of them will be able to modify the pH of the base water. It is then expected that the pH is 7. In this case, a strong base conjugated cation is dissolved, it will be a weak acid that does not influence the pH. And the conjugated anion of strong acid, a weak base, does not change the pH either.
- On the other hand, if a salt whose conjugated cation of weak base is dissolved, it is a strong acid. Whereas, if the anion is conjugated to a strong acid, it will be a weak base incapable of reacting with water. What will predominate will be the reaction of the strong conjugated acid with the water donating protons and lowering the pH.
- The reverse occurs if the cation is a strong base conjugate (weak acid) and the anion is a weak acid conjugate (strong base). What will predominate will be the reaction of the strong base with the water, increasing the production of OH- and consequently increasing the pH.
- Finally, it may be the case where anion and cation are strong bases and acids that can influence the pH. In this case, it must be observed which reaction predominates over the other, if the formation of OH- or that of H3O +. To do this, we must resort to the acidity and basicity constants: if the acidity constant is greater than the basicity constant, the pH will be less than 7. Conversely, if the basicity constant predominates over the acidity constant, the pH will be higher than 7. In short, when both constants are equal, the pH = 7 and is similar to the first case studied.
Topics in Hydrolysis

